Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Anatomy of the Breast
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Anatomy of the Oesophagus |Anatomy of the Diaphragm |Anatomy of Large Bowel |Anatomy of Small Bowel |Anatomy of the Biliary system |Anatomy of the Eye |Anatomy of the Larynx |Anatomy of the Ear |Anatomy of the Pharynx |Anatomy of the Nose |Anatomy of Male Genitalia |Anatomy of Breast |Anatomy of the Stomach |Anatomy of the Rectum |Anatomy of the Spleen |Anatomy of the Liver
Introduction
The breast is a complex structure composed of glandular tissue, adipose (fat) tissue, connective tissue, and skin. It plays key roles in lactation, sexual function, and has significant clinical relevance in health and disease. Detailed knowledge of breast anatomy is essential in fields such as medicine, surgery, and radiology.
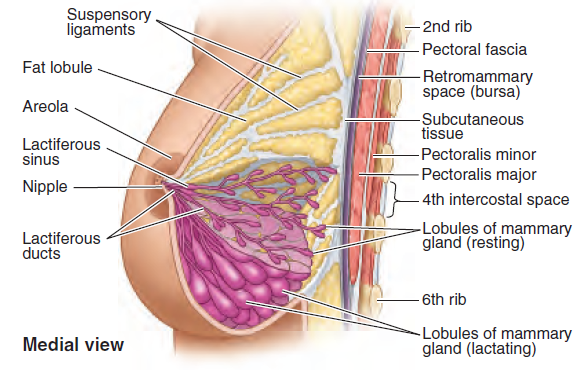
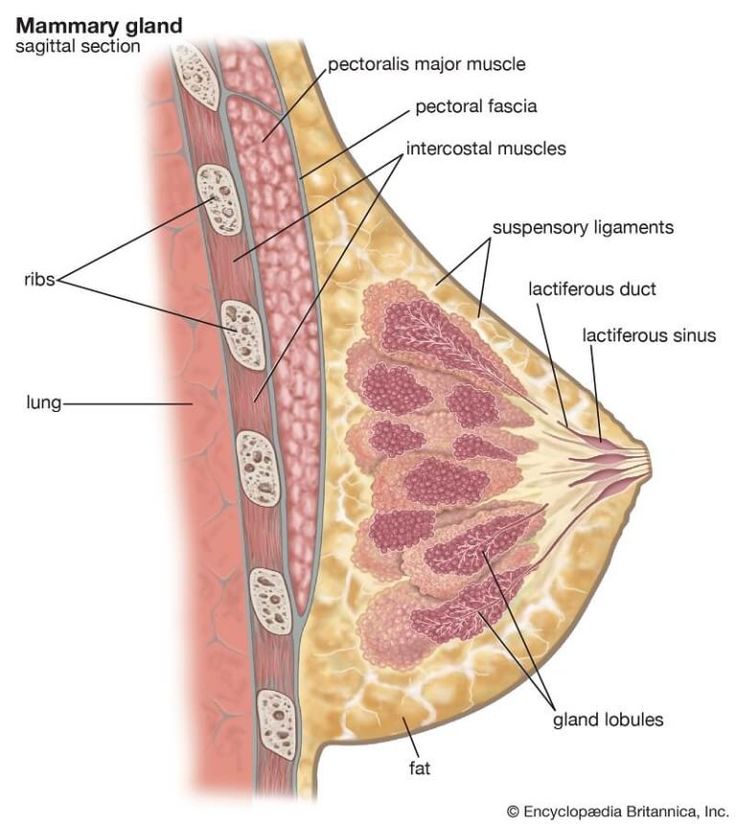
External Anatomy
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue:
- The outermost layer is the skin, which varies in thickness and contains sweat and sebaceous glands.
- The subcutaneous layer is rich in adipose tissue that determines the size and shape of the breast.
- Nipple and Areola:
- Nipple: The central projection that contains smooth muscle fibers, allowing for erection in response to stimuli.
- Areola: The pigmented area surrounding the nipple, which contains Montgomery glands that lubricate and protect the nipple during breastfeeding.
Internal (Glandular) Anatomy
- Lobes and Lobules:
- The breast is divided into 15–20 lobes arranged radially around the nipple.
- Each lobe is composed of smaller lobules, which are clusters of milk-producing alveoli.
- Ductal System:
- The lobules drain into a network of lactiferous ducts that converge centrally toward the nipple.
- During lactation, these ducts transport milk from the alveoli to the nipple surface.
- Connective Tissue:
- Cooper’s Ligaments: Fibrous bands that extend from the dermis to the pectoral fascia, providing structural support and maintaining the shape of the breast.
- The fibrous stroma intermingles with adipose and glandular tissues, contributing to the breast’s consistency.
Vascular Supply
- Arterial Supply:The primary blood supply comes from the internal thoracic (mammary) artery, lateral thoracic artery, and intercostal arteries.
- Venous Drainage:Venous return is provided by the superficial and deep venous systems, draining into the axillary and internal thoracic veins.
Lymphatic Drainage
- Lymph Nodes: The majority of lymphatic drainage from the breast is directed to the axillary lymph nodes, which are critical in staging breast cancer. Additional drainage occurs to the internal mammary (parasternal) lymph nodes and, less commonly, to the supraclavicular nodes.
Innervation
- Nerve Supply: Sensory innervation is primarily via the lateral and anterior cutaneous branches of the intercostal nerves. The nipple-areolar complex is richly innervated, contributing to erogenous sensation and reflexive responses.
Embryological Development
The breasts begin developing during the embryonic stage as mammary ridges along the ventral surface. By puberty, hormonal influences stimulate the growth and differentiation of glandular tissue, forming the mature structures capable of lactation.
Clinical Significance
- Breast Cancer:
- Understanding the ductal-lobular anatomy and lymphatic drainage is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.
- Benign Conditions:
- Fibroadenomas, cysts, and mastitis are examples of common benign breast conditions that involve various components of breast tissue.
- Reconstructive Surgery:
- Detailed knowledge of breast anatomy is vital for procedures such as lumpectomy, mastectomy, and reconstructive surgeries after cancer treatment.
Conclusion
The male and female breast share a complex anatomical framework of skin, glandular tissue, ducts, supportive ligaments, vasculature, lymphatics, and innervation. Detailed understanding of these structures provides a foundation for clinical evaluation, surgical intervention, and further study in health sciences.