Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
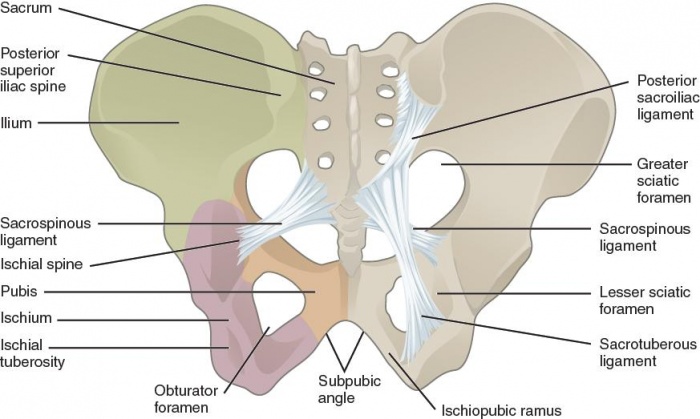
Pelvic fractures
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects:
|Fractured Neck of Femur
|Fractured Shaft Femur
|Supracondylar Femur Fractures
|Supracondylar Humerus Fractures
|Femoral fractures
|Fractured Tibia and Fibula
|Pelvic fractures
Pelvic Fractures 🦴🚨 are high-risk injuries often associated with major trauma, haemorrhage, and multi-organ injury.
👉 Mortality ≈10% in closed fractures, up to 50% in open fractures.
Always consider associated injuries and hidden blood loss → involve the major trauma centre early.
📖 About
⚙️ Aetiology
🩺 Clinical Features
🔎 Predictors of Major Haemorrhage
📊 Tile Classification
Type A Stable: avulsion fractures, isolated pubic ramus, iliac wing fractures. Often low-energy, muscle avulsion (e.g. AIIS → rectus femoris, ASIS → sartorius, ischial tuberosity → hamstrings).
Type B Rotationally unstable but vertically stable.
B1 = “open book” (AP compression).
B2 = ipsilateral compression (overriding pubic bones).
B3 = contralateral compression (pubic rami fracture one side + SI compression other side).
Type C Rotationally + vertically unstable. Ring disrupted in ≥2 places. Massive blood loss, high mortality.
C1 unilateral, C2 bilateral, C3 with acetabular involvement.
🧾 Simple Classification
⚠️ Complications
🧪 Investigations
💊 Management
📌 OSCE / Exam Pearls
📚 References