Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
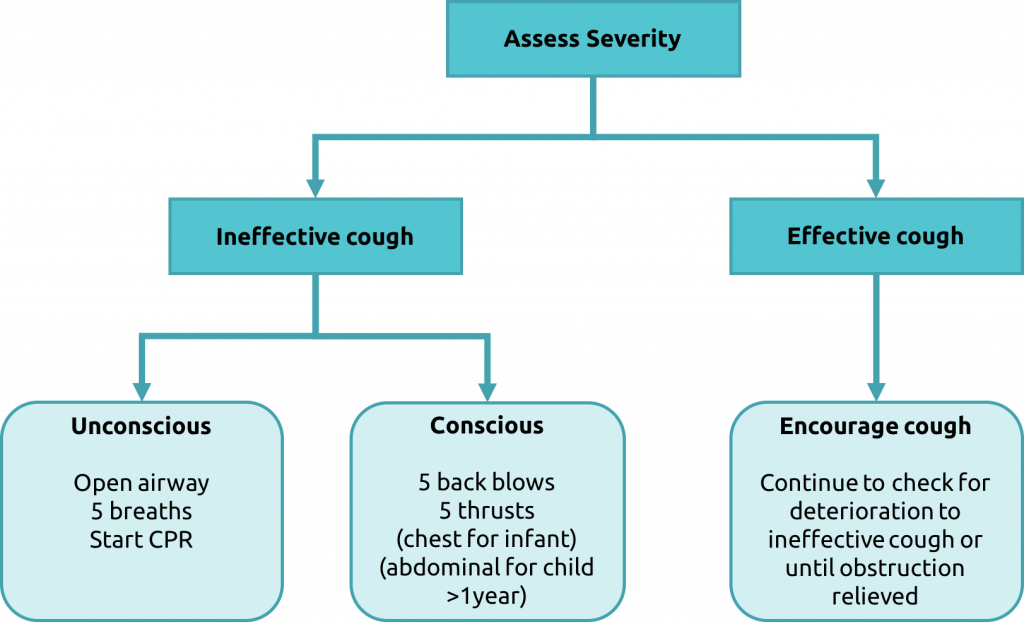
Resuscitation - Choking Algorithm
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: Atropine |Acute Anaphylaxis |Basic Life Support |Advanced Life Support |Adrenaline/Epinephrine |Acute Hypotension |Cardiogenic shock |Distributive Shock |Hypovolaemic or Haemorrhagic Shock |Obstructive Shock |Septic Shock and Sepsis |Shock (General Assessment) |Toxic Shock Syndrome
Choking occurs when an object, food, or liquid obstructs the airway, preventing normal breathing. ⚠️ It can be a life-threatening emergency requiring immediate intervention. This guide covers recognition, first aid, and prevention strategies for both adults and children.
👀 Recognizing Choking
- Signs in Adults and Children:
- Inability to speak or cry out.
- Difficulty or noisy breathing.
- Weak, ineffective coughing or no cough.
- Clutching the throat (universal choking sign).
- Cyanosis (bluish skin) from hypoxia.
- Loss of consciousness if unresolved.
🧍 First Aid for Choking in Adults
- Encourage Coughing: If able to cough forcefully, encourage until object expelled.
- Heimlich Maneuver (Abdominal Thrusts):
- Stand behind, wrap arms around waist.
- Fist just above navel, grasp with other hand.
- Perform quick upward thrusts.
- Repeat until object expelled or collapse occurs.
- Call Emergency Services 📞 if unable to breathe/speak or loss of consciousness.
- CPR ❤️: If unconscious and not breathing, begin CPR until help arrives.
🧒 First Aid for Choking in Children (>1 year)
- Encourage coughing if effective.
- Heimlich Maneuver: Kneel behind small child, stand for larger. Apply thrusts as with adults.
- Call emergency services if airway not cleared.
- Start CPR if unconscious.
👶 First Aid for Choking in Infants (<1 year)
- Back Blows & Chest Thrusts:
- Hold infant face down on forearm, head supported.
- Give up to 5 back blows between shoulder blades.
- If not effective → turn face up, give 5 chest thrusts (two fingers, below nipple line).
- Repeat cycles until object expelled or infant collapses.
- Call emergency services immediately if unresolved.
- Begin CPR if unconscious and not breathing.
🛡️ Prevention of Choking
- Adults:
- Chew thoroughly, eat slowly.
- Avoid talking/laughing while eating.
- No eating while walking, running, or driving.
- Limit alcohol during meals.
- Children:
- Supervise meals, cut food into small pieces.
- Avoid nuts, popcorn, hard sweets in toddlers.
- Teach safe chewing and no talking with food in mouth.
- Keep small objects and toys out of reach.
📌 Summary
Choking is a life-threatening emergency. ✅ Recognize the signs quickly. ✅ Apply the right first aid (adult, child, or infant). ✅ Call emergency services early. ✅ Prevent by safe eating practices and child supervision.
👶 Choking in Children