Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Wolff-Parkinson White syndrome (WPW) AVRT
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Wolff-Parkinson White syndrome (WPW) AVRT |Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome AVRT |Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) |Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia AVNRT |Atrial Flutter |Atrial Fibrillation |Sinus Tachycardia |Sinus Arrhythmia |Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia |Resuscitation - Adult Tachycardia Algorithm
⚡ Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is caused by an accessory conduction pathway (the Bundle of Kent) that bypasses the AV node. This leads to early ventricular activation and a reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), increasing the risk of rapid arrhythmias 🚨.
ℹ️ About WPW Syndrome
- 🧩 Involves an abnormal electrical connection (Bundle of Kent) between atrium & ventricle.
- ⚡ Bypasses AV node → fast conduction & early ventricular depolarisation (pre-excitation).
- 🔄 Can trigger AVRT (narrow or wide complex tachycardia depending on pathway).
🧠 Pathophysiology & Mechanisms
- Normally ➝ AV node delays conduction ⏱.
- In WPW ➝ accessory pathway conducts in both directions ➝ reentry circuits 🔄.
- 🚨 AF with WPW: rapid conduction down accessory pathway can cause VF (life-threatening).
🫀 Associations
- ASD (septum secundum)
- Ebstein anomaly
- HCM
- MVP
👨⚕️ Clinical Presentation
- May be asymptomatic despite classic ECG findings 📈.
- Symptoms: 💓 palpitations, 😵 syncope, dizziness.
- 🚨 Rarely → sudden cardiac death (rapid AF → VF).
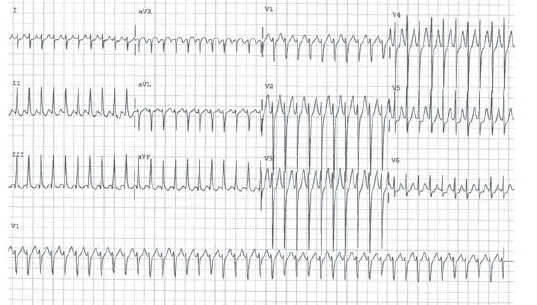
📈 ECG Findings
- Resting ECG:
- 🙈 Concealed pathway: Normal ECG, no delta wave.
- 👀 Manifest pathway: Short PR + slurred delta wave.
- Arrhythmias:
- 🔄 AVRT (SVT): usually narrow complex.
- ⚡ AF with pre-excitation: irregular wide rhythm + delta waves → risk of VF.
📊 ECG Examples - WPW
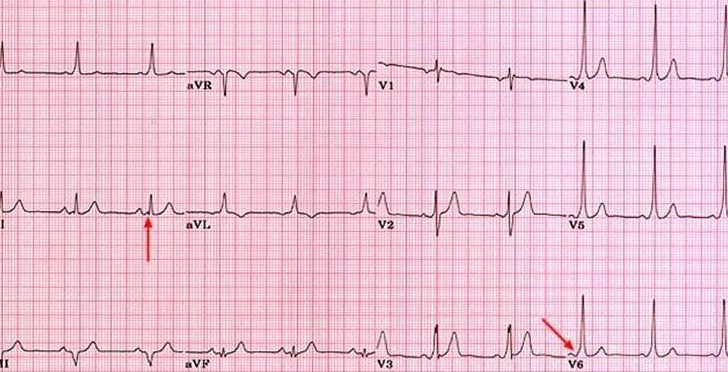
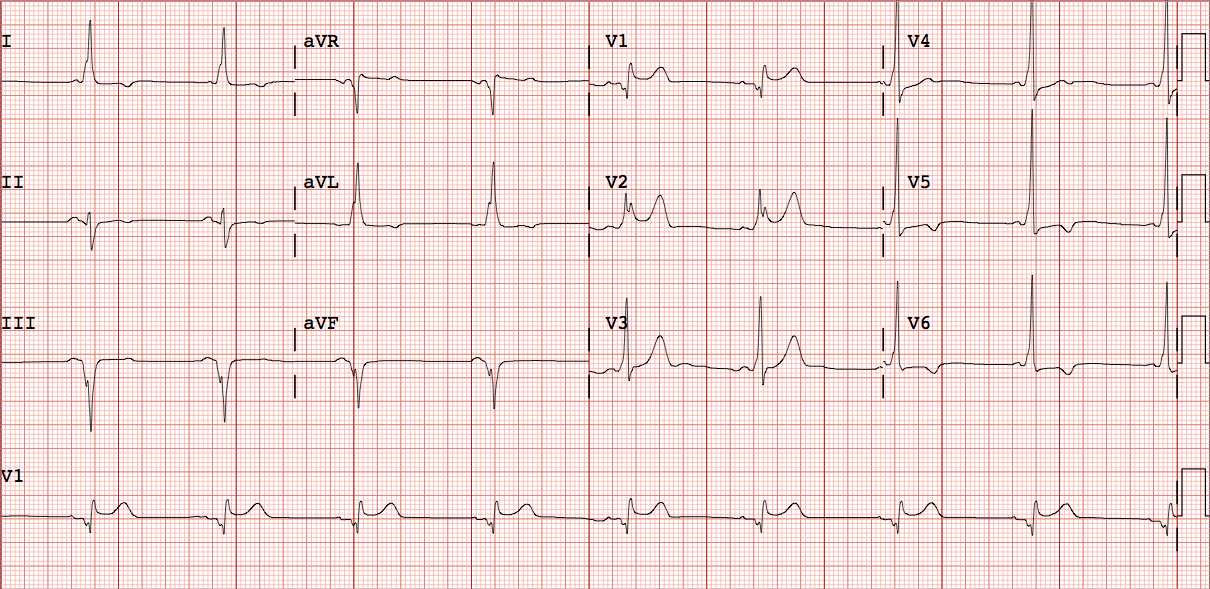
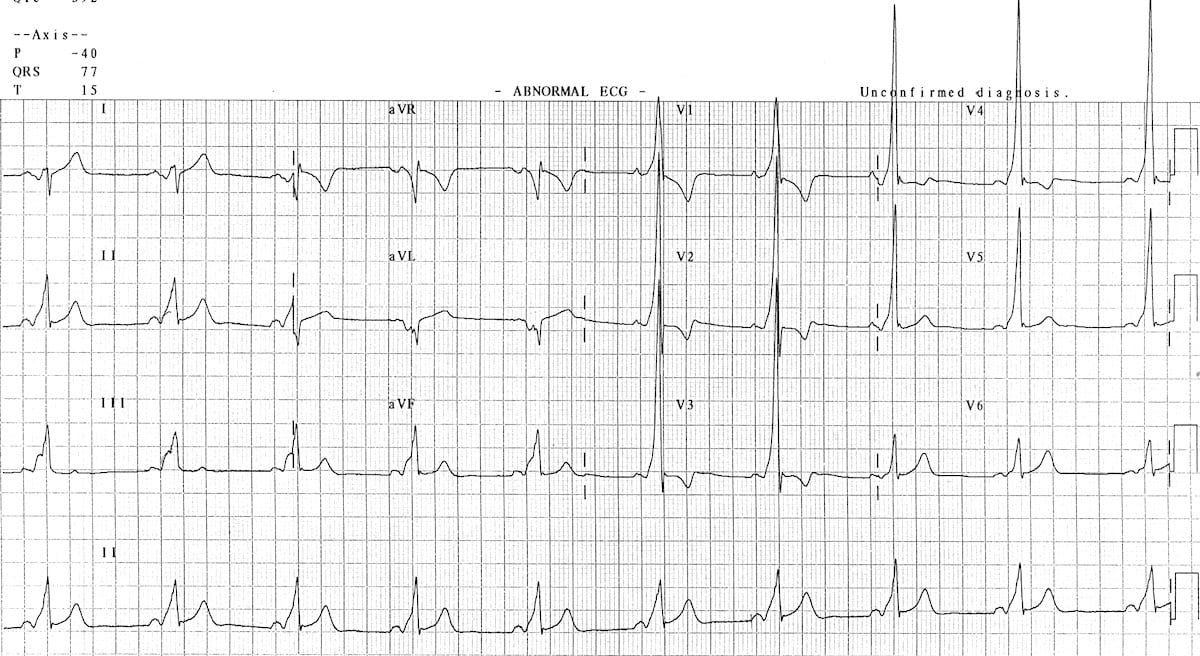
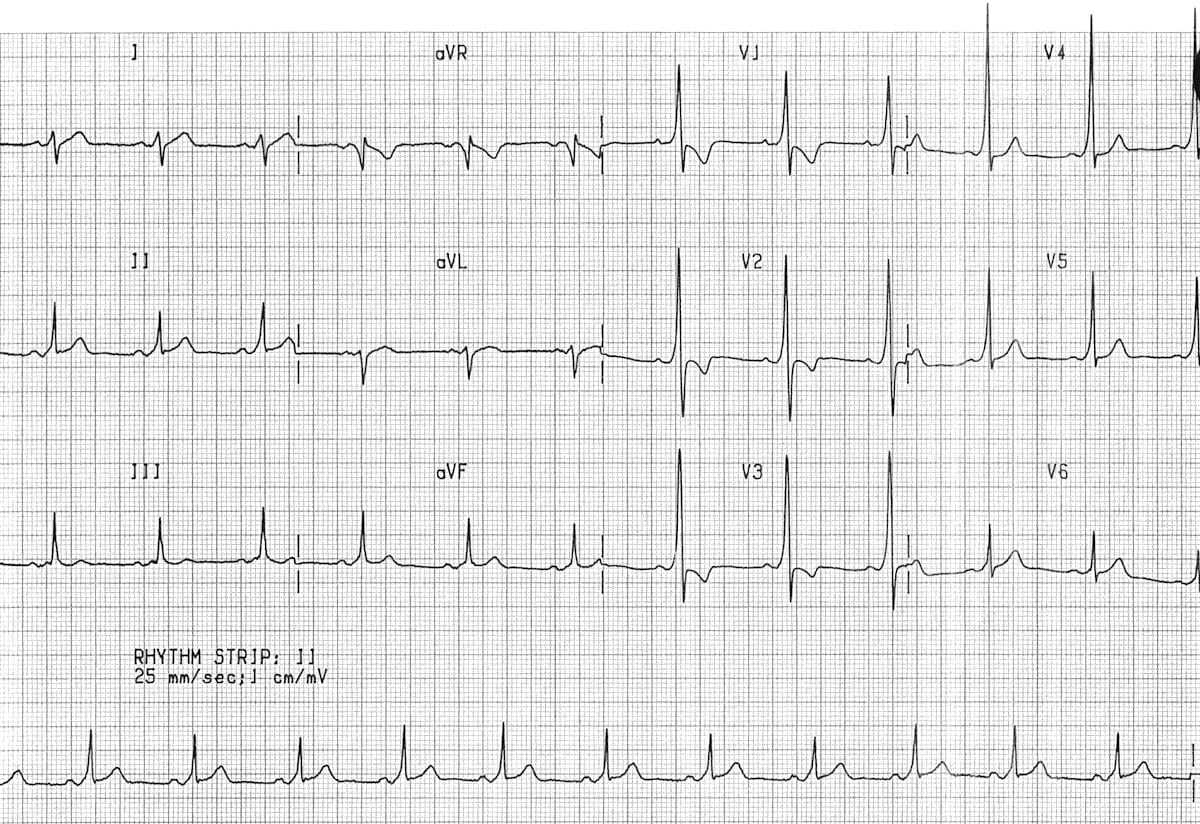
📊 ECG Example - AVNRT
🔬 Investigations
- 🧪 Bloods: FBC, U&E, TFTs, CRP
- 📈 ECG: look for pre-excitation, delta waves
- 🫀 Echo/MRI: check structural heart disease
- ⚡ EP studies: localise accessory pathway, plan ablation
🚨 Atrial Fibrillation in WPW

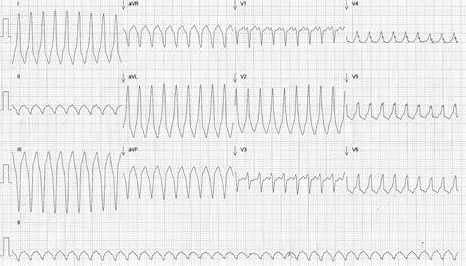

⚠️ Warning: In WPW + AF ➝ ❌ avoid Adenosine, Digoxin, Beta Blockers, CCBs ➝ they increase conduction via the accessory pathway and worsen ventricular response.
🏥 Acute Management Scenarios
- Regular Narrow Complex Tachycardia (AVRT SVT):
- 🧘 Vagal manoeuvres first.
- 💉 Adenosine if stable. 🚨 If unstable → DC cardioversion.
- Pre-excited AF:
- 📈 Irregular wide rhythm, delta waves, HR >200 bpm.
- 🚨 If unstable → immediate DC shock.
- 💊 Options: IV Procainamide, Ibutilide, Propafenone, Flecainide.
- ❌ Avoid AV nodal blockers (Digoxin, BB, CCB, Adenosine).
🔧 Definitive Management
- 🎯 Radiofrequency catheter ablation → first-line in recurrent SVT/pre-excited AF.
- ✅ Success rate ~95%, reduces symptoms & SCD risk.
- ⚠️ Rare complication (1%): AV block → pacemaker required.
🩺 Case 1 — Symptomatic Tachycardia
A 24-year-old man presents with sudden-onset palpitations and light-headedness after exercise. Pulse is 180 bpm, BP 120/80 mmHg. ECG during the episode shows a narrow-complex tachycardia, and a previous ECG demonstrated a short PR interval and delta wave consistent with WPW. Management: 💊 Stable SVT in WPW is managed with procainamide or flecainide; radiofrequency ablation offers a curative option. Avoid: ❌ AV nodal blockers (adenosine, verapamil, beta-blockers, digoxin) as they can worsen conduction down the accessory pathway.
🩺 Case 2 — Pre-excited AF
A 32-year-old woman presents with palpitations and chest tightness. ECG shows atrial fibrillation with irregular broad-complex tachycardia and varying QRS morphology — consistent with AF in WPW. She is haemodynamically stable. Management: ⚡ Procainamide or ibutilide are preferred; cardioversion if unstable. Electrophysiology referral for ablation. Avoid: ❌ Never use AV nodal blockers (adenosine, verapamil, beta-blockers, digoxin) in pre-excited AF — can trigger VF.
🩺 Case 3 — Incidental Finding
A 19-year-old student attends for a routine health check before joining the army. He is asymptomatic, but ECG shows a short PR interval and delta wave. Management: 🩺 No acute treatment needed; counsel regarding risk of arrhythmias. Refer to cardiology/electrophysiology for risk stratification (exercise testing, EP study). Ablation may be considered in high-risk occupations or competitive athletes. Avoid: ❌ Ignoring the finding in high-risk settings (e.g. pilots, military, professional athletes). Avoid AV nodal blockers if arrhythmia occurs.