Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Hepatorenal syndromes
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) / Acute Renal Failure |Chronic liver disease |Cirrhosis |Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) |Liver Function Tests |Ascites Assessment and Management |Budd-Chiari syndrome |Autoimmune Hepatitis |Primary Biliary Cirrhosis |Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis |Wilson disease | |Hereditary Haemochromatosis |Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency |Non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) |Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis |Alcoholism and Alcoholic Liver Disease
About
- Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS): A severe form of acute kidney failure occurring in patients with advanced liver disease and ascites. It is a life-threatening complication commonly associated with cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, or fulminant liver failure.
- HRS is now classified using the International Club of Ascites (ICA) system, aligning with the Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) framework for a more nuanced understanding of renal dysfunction in liver disease.
Classification
The new ICA classification integrates traditional Type 1 and Type 2 HRS into a more detailed system based on the severity and progression of kidney dysfunction, facilitating earlier detection and tailored management.
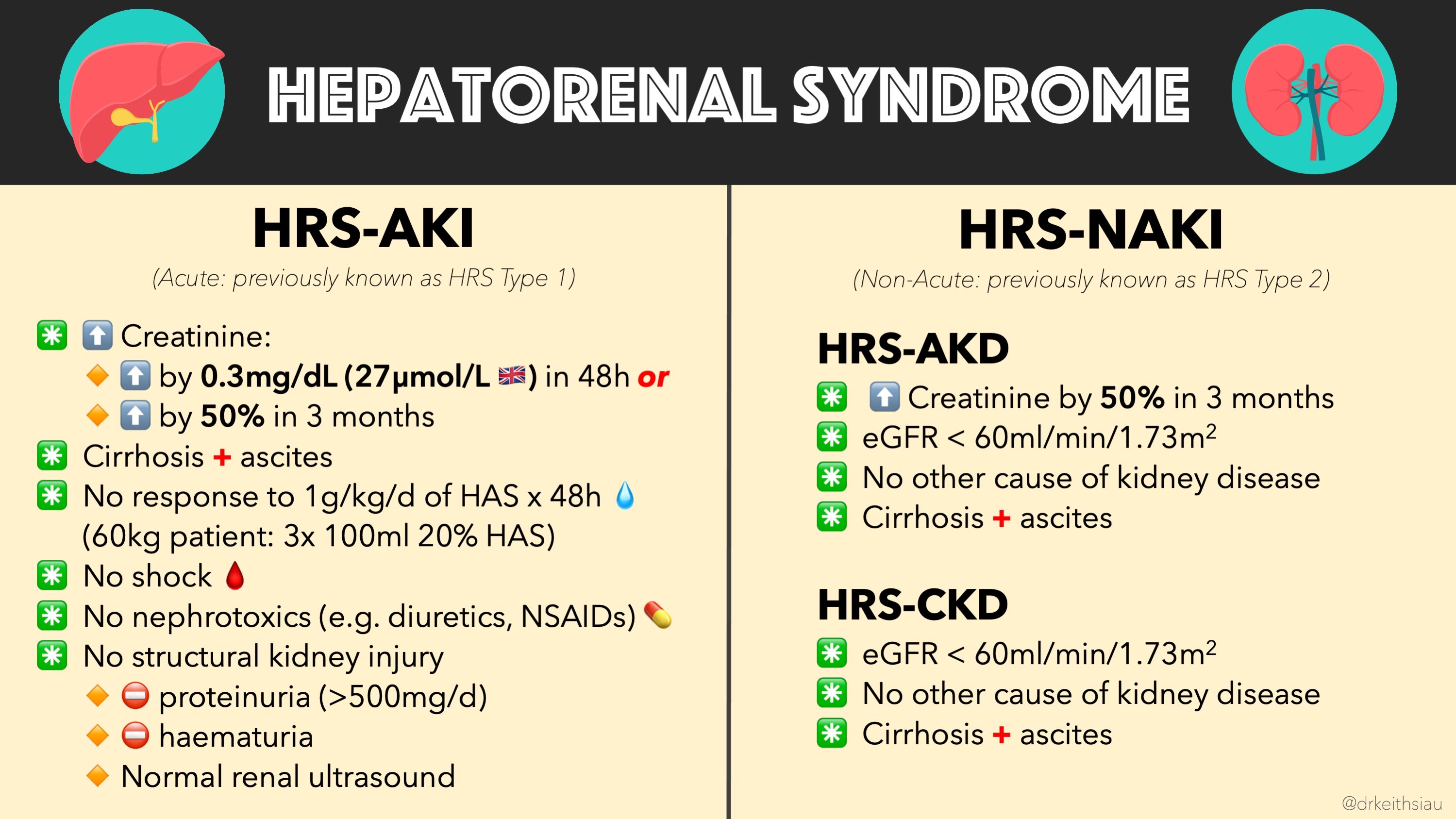
- HRS-AKI (Hepatorenal Syndrome - Acute Kidney Injury):
- Characterized by a rapid increase in serum creatinine, following AKI criteria.
- Subdivided into:
- Stage 1: Increase in serum creatinine ≥0.3 mg/dL within 48 hours or ≥1.5 times baseline within 7 days.
- Stage 2: Further elevation of serum creatinine by ≥2 times baseline.
- Stage 3: Serum creatinine >4.0 mg/dL or initiation of renal replacement therapy.
- HRS-CKD (Hepatorenal Syndrome - Chronic Kidney Disease):
- Represents stable, long-term impairment of renal function.
- Associated with diuretic-resistant ascites and persistent renal dysfunction.
Aetiology
- Nitric Oxide (NO): Excessive production leads to splanchnic vasodilation, reducing systemic vascular resistance and effective arterial blood volume.
- Splanchnic Vasodilation: Decreases effective blood volume, triggering compensatory renal vasoconstriction to maintain blood pressure.
- Renal Vasoconstriction: Reduces renal blood flow, causing oliguria and acute kidney injury without structural kidney damage.
- Systemic Inflammation: Elevated inflammatory cytokines contribute to vasodilation and renal dysfunction.
Clinical Features
- Oliguria: Significant reduction in urine output, often less than 500 mL per day.
- Hypotension: Persistently low blood pressure due to decreased systemic vascular resistance.
- Signs of Chronic Liver Disease: Jaundice, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and other manifestations alongside renal symptoms.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Hyponatremia and hyperkalemia may be present.
Comparing Classifications
The table below contrasts the traditional classification (Type 1 and Type 2) with the new ICA classification (HRS-AKI and HRS-CKD).
| Feature | Traditional Classification | New ICA Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Classification Basis | Type 1 and Type 2 based on onset and severity. | HRS-AKI and HRS-CKD based on AKI framework and chronicity. |
| Onset | Type 1: Rapid onset.
Type 2: Gradual onset. |
HRS-AKI: Rapid increase in serum creatinine.
HRS-CKD: Chronic, stable renal dysfunction. |
| Serum Creatinine | Type 1: Doubles to >2.5 mg/dL in <2 weeks.
Type 2: Slowly rising. |
HRS-AKI: Staged per AKI criteria.
HRS-CKD: Elevated and stable over months. |
| Urinary Output | Type 1: Marked oliguria.
Type 2: Moderate reduction. |
HRS-AKI: Varies with stage.
HRS-CKD: Persistent reduction. |
| Associated Features | Type 1: Precipitated by events like GI bleeding.
Type 2: Diuretic-resistant ascites. |
HRS-AKI: Similar precipitating events under AKI framework.
HRS-CKD: Diuretic-resistant ascites. |
| Prognosis | Type 1: Poor without transplant.
Type 2: Better but still poor. |
HRS-AKI: Varies with AKI stage; high mortality in advanced stages.
HRS-CKD: Better than HRS-AKI but still guarded. |
| Survival without Liver Transplant | Type 1: Median <2 weeks.
Type 2: Median ~6 months. |
HRS-AKI: Dependent on AKI stage; lower survival in higher stages.
HRS-CKD: Median survival better than HRS-AKI. |
| Key Characteristic | Type 1: Acute renal failure.
Type 2: Chronic renal dysfunction. |
HRS-AKI: Acute changes per AKI.
HRS-CKD: Chronic impairment. |
Investigations
- Laboratory Tests:
- Rising Urea and Creatinine: Indicative of renal failure without significant structural kidney damage.
- No Proteinuria: Helps differentiate HRS from intrinsic renal diseases.
- Low Urinary Sodium: Typically <10 mmol/L, reflecting sodium conservation by the kidneys.
- Urine/Plasma Osmolarity: Ratio usually >1.5, indicating concentrated urine despite impaired function.
- Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasonography: To rule out other causes of renal dysfunction such as obstruction.
- Renal Doppler Studies: May show reduced renal blood flow.
- Exclusion of Other Causes: Essential to confirm HRS by ruling out intrinsic renal diseases.
Management
- Albumin Infusions: Expand plasma volume and improve renal perfusion. Typical dosing: 1 g/kg on the first day, followed by 20-40 g/day as needed.
- Terlipressin: A vasopressor counteracting splanchnic vasodilation to improve renal blood flow. Standard dosing: 2 mg every 4-6 hours, titrated based on response.
- Nitric Oxide Inhibitors: Agents like midodrine may be combined with other vasoconstrictors to enhance efficacy.
- Diuretics: Often discontinued to prevent further intravascular volume depletion.
- Haemodialysis: Generally not indicated unless severe electrolyte imbalances or volume overload are present.
- Liver Transplantation: The definitive treatment offering the best chance for renal recovery and overall survival.
- Vasoconstrictor Therapy: Combination of vasopressors (e.g., terlipressin) and albumin is first-line therapy for HRS-AKI.
- Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS): May be considered in select cases to reduce portal hypertension, though its role in HRS is limited.
Type II Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS)
- Characterized by less severe but more chronic renal dysfunction compared to Type I.
- Primary features include diuretic-resistant ascites, where standard diuretic therapy fails, leading to persistent fluid accumulation.
- Renal dysfunction progresses more slowly, allowing for potential stabilization with appropriate medical management.
- Despite a gradual course, Type II HRS carries significant morbidity and a poor prognosis without liver transplantation.
- Treatment strategies include vasoconstrictors, albumin infusions, and consideration of liver transplantation for eligible patients.
References
Cases — Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS)
- Case 1 — Type 1 (rapid onset) ⚡: A 58-year-old man with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis is admitted with tense ascites and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Within 2 weeks, his creatinine rises from 95 → 340 µmol/L despite fluid resuscitation. Diagnosis: HRS type 1 (acute, rapidly progressive). Managed with IV albumin, terlipressin, and evaluation for liver transplant.
- Case 2 — Type 2 (chronic/insidious) 🐢: A 62-year-old woman with hepatitis C cirrhosis presents with gradually worsening ascites resistant to diuretics. Renal function is impaired (creatinine 160 µmol/L) but stable over months. No response to fluid challenge. Diagnosis: HRS type 2 (slowly progressive, linked to refractory ascites). Managed with diuretic withdrawal, albumin infusions, vasoconstrictors, and transplant referral.
- Case 3 — Precipitated by variceal bleed 💉: A 55-year-old man with Child-Pugh C cirrhosis is admitted with massive variceal haemorrhage. Despite haemostasis, his renal function deteriorates rapidly with oliguria and rising urea/creatinine. No evidence of shock or nephrotoxins. Diagnosis: HRS triggered by GI bleed. Managed with vasoconstrictors (terlipressin), albumin, and critical care support.
Teaching Point 🩺: Hepatorenal Syndrome is a functional renal failure in advanced cirrhosis, due to intense renal vasoconstriction and splanchnic vasodilatation. Key clues: cirrhosis, ascites, renal impairment, no structural kidney disease. Two main patterns: Type 1 (rapid, severe, often after infection/bleed) and Type 2 (slower, with refractory ascites). Definitive treatment is liver transplantation.