Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Iron deficiency Anaemia
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Iron deficiency Anaemia |Haemolytic anaemia |Macrocytic anaemia |Megaloblastic anaemia |Microcytic anaemia |Myelodysplasia |Myelofibrosis
⚠️ Iron deficiency anaemia in an older patient = gastrointestinal malignancy until proven otherwise. 👉 Always investigate with both upper GI endoscopy and colonoscopy.
📖 About
- Always consider gastrointestinal malignancy until excluded 🚨
🧬 Aetiology
- Poor intake, excess loss, or increased utilisation (most iron is normally reused).
- There is a latent period of iron loss before anaemia becomes clinically evident.
🩸 Causes
- Gastrointestinal blood loss (most common in adults)
- Menstrual blood loss
- Pregnancy (↑ requirements)
- Dietary deficiency
- Hookworm 🪱 (commonest worldwide)
- Schistosomiasis
- Paterson–Brown–Kelly (Plummer–Vinson) syndrome
🩺 Clinical Features
- Fatigue, pallor, exertional breathlessness
- Koilonychia – spoon-shaped nails
- Pallor of conjunctiva & palmar creases
- Brittle nails, hair loss, cheilosis, glossitis
- Flow murmurs (high-output state)
- Pica – craving ice (pagophagia) or clay (geophagia)
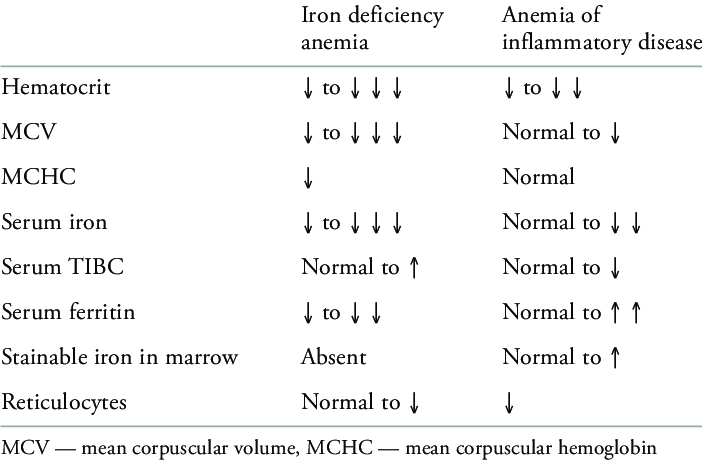
🔎 Investigations
- Microcytic, hypochromic anaemia (low MCV, hypochromic RBCs, low reticulocytes)
- Low serum ferritin (best marker unless infection/inflammation present)
- Plasma iron ↓, TIBC ↑
- Soluble transferrin receptor ↑ (helps distinguish from anaemia of chronic disease)
- Transferrin saturation < 15% → impaired Hb synthesis
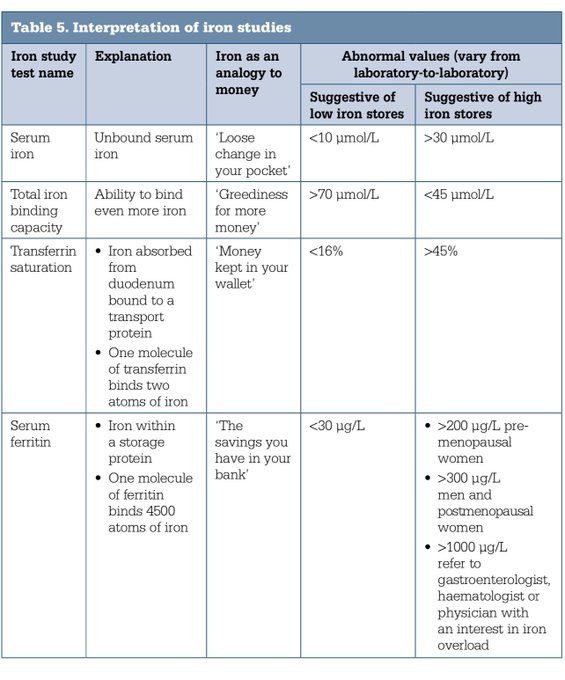
📊 Key Components of Iron Studies
- Serum Iron: 10–30 µmol/L (55–160 µg/dL)
- TIBC: 45–70 µmol/L (250–450 µg/dL)
- Transferrin Saturation: 20–50%
- Ferritin: 15–300 µg/L (men), 15–200 µg/L (women)
🧾 Interpreting Iron Studies
The pattern of iron studies helps distinguish IDA from anaemia of chronic disease and iron overload states:
| Condition | Serum Iron | TIBC | Transferrin Sat | Ferritin | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron Deficiency Anaemia | Low | High | Low | Low | Insufficient iron (dietary, chronic blood loss, pregnancy) |
| Anaemia of Chronic Disease | Low/Normal | Low | Low | Normal/High | Iron sequestered in macrophages due to inflammation |
| Haemochromatosis | High | Low/Normal | High | High | Genetic ↑ absorption → organ damage risk |
| Secondary Iron Overload | High | Low/Normal | High | High | Commonly post-multiple transfusions |
| Iron Deficiency (pre-anaemia) | Low | High | Low | Low | Early iron depletion before anaemia develops |
| Sideroblastic Anaemia | Normal/High | Normal/Low | Normal/High | High | Ineffective erythropoiesis – iron not incorporated |
🧪 Additional Investigations
- Rectal exam, proctoscopy → exclude rectal tumour, piles
- Upper GI endoscopy ± jejunal biopsy → ulcers, coeliac disease
- Colonoscopy → polyps, malignancy, colitis
- Serology → Anti-endomysial, Anti-tTG (coeliac)
- Stool/urine → parasites
- Gynae/urology → menorrhagia or haematuria causes
- Small bowel MRI or capsule endoscopy → obscure bleeding
- Meckel’s scan → ectopic gastric mucosa
- Angiography → severe occult bleeding
💊 Oral iron: Once daily FeSO₄ (or alternate day) is usually sufficient. ❌ Stop 3x/day dosing – only ↑ side effects (constipation, nausea).
💊 Management
- Identify & treat the cause (GI malignancy until excluded).
- FeSO₄ 200 mg once daily or alternate days × 6 months. Expect Hb ↑ ~1 g/dL/week with response.
- Parenteral iron if intolerance to oral iron or need for rapid correction (e.g. pre-op).
- Blood transfusion if severe anaemia with symptoms or haemodynamic compromise.
Cases — Iron Deficiency Anaemia (IDA)
- Case 1 — Menorrhagia in a Young Woman: A 28-year-old woman presents with fatigue, pallor, and hair thinning. She reports heavy menstrual periods lasting 7 days. FBC: Hb 9.4 g/dL, MCV 71 fL, ferritin 7 µg/L. Diagnosis: IDA secondary to menorrhagia.
- Case 2 — Elderly Man with Occult GI Bleeding: A 74-year-old man complains of lethargy and exertional dyspnoea. No overt bleeding. Hb 8.2 g/dL, MCV 65 fL, ferritin 9 µg/L. FIT test positive, colonoscopy reveals a right-sided colonic adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis: IDA from chronic gastrointestinal blood loss (malignancy).
- Case 3 — Child with Poor Diet: A 5-year-old boy has irritability, pica (soil craving), and poor growth. Diet is low in meat and vegetables, dominated by cow’s milk. Hb 7.6 g/dL, MCV 62 fL, ferritin 5 µg/L. Diagnosis: Nutritional IDA in childhood.
- Case 4 — Post-Gastrectomy Malabsorption: A 60-year-old woman who had partial gastrectomy 10 years ago presents with fatigue and brittle nails. Hb 8.9 g/dL, MCV 68 fL, ferritin 11 µg/L. Normal B12 and folate. Diagnosis: IDA secondary to impaired absorption (post-gastrectomy).
- Case 5 — Pregnancy-Associated IDA: A 30-year-old woman at 28 weeks gestation reports tiredness and shortness of breath. Hb 9.0 g/dL, MCV 69 fL, ferritin 10 µg/L. She has not been taking iron supplementation. Diagnosis: IDA due to increased requirements in pregnancy.
Teaching Commentary 🩸
IDA is the most common anaemia worldwide. Core labs: low Hb, microcytosis, low ferritin. Causes are diverse: - Blood loss (menorrhagia, GI cancer, peptic ulcer, hookworm), - Poor intake (children, elderly, restrictive diets), - Malabsorption (gastrectomy, coeliac disease), - Increased demand (pregnancy, growth). Clinical features include fatigue, pallor, glossitis, angular cheilitis, koilonychia, and pica. Always treat the cause and replenish iron stores (oral ferrous sulfate/fumarate/gluconate, or IV iron if malabsorptive or intolerant). In UK practice, unexplained IDA in men or postmenopausal women mandates urgent GI investigation for malignancy.