Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Assessing Abdominal Pain
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects:Acute Cholecystitis |Acute Appendicitis |Chronic Peritonitis |Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm |Ectopic Pregnancy |Acute Cholangitis |Acute Abdominal Pain/Peritonitis |Assessing Abdominal Pain |Penetrating Abdominal Trauma |Acute Pancreatitis |Acute Diverticulitis
⚠️ Pain may be absent or muted in certain high-risk groups — elderly patients, those on long-term steroids, diabetics, and the very frail. Always think: is the patient moribund/in extremis? If so → follow ABC, call for senior/surgical help early, gain IV access, give oxygen, start IV crystalloids, provide analgesia, and send urgent bloods (including lactate, FBC, U&E, amylase, and cross-match if haemorrhage is suspected). 👉 If shocked with bleeding → get 2 wide-bore lines, activate major haemorrhage protocol, consider urgent O negative blood. 👉 If septic → IV antibiotics + fluids without delay.
| 🚑 Acute Abdominal Pain – Emergency Management Summary |
|---|
|
📖 Acute Abdomen – Key Principles
- Sudden onset severe abdominal pain (<24h) → always assume potentially lethal pathology until proven otherwise
- Expert assessment + early surgical involvement crucial
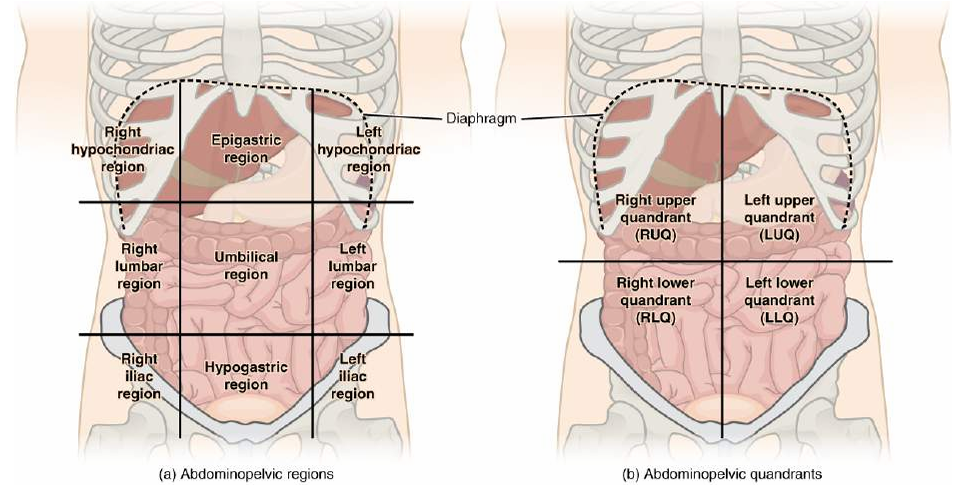
- Pain localisation often follows embryological origin:
- 🌐 Foregut → Epigastrium
- 🌐 Midgut → Peri-umbilical
- 🌐 Hindgut → Below umbilicus
🧠 Pathophysiological Background
- Parietal peritoneum richly innervated → inflammation causes localised pain, guarding & rigidity
- Visceral pain → poorly localised, dull (e.g. appendicitis starts peri-umbilical)
- When parietal peritoneum becomes involved → pain localises (e.g. appendicitis to RIF at McBurney’s point)
- Always examine hernial orifices to exclude strangulated hernia
🔎 Common Causes of Acute Abdominal Pain
| Cause | Clinical Features | Diagnostic Tests | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appendicitis | RIF pain, anorexia, fever, rebound tenderness | FBC, US/CT | Appendicectomy ± antibiotics |
| Cholecystitis | RUQ pain, post-prandial, fever | US, LFTs | Cholecystectomy |
| Pancreatitis | Epigastric pain radiating to back, vomiting | Amylase/lipase, CT | IV fluids, analgesia, NBM |
| Ectopic Pregnancy | Lower pain, bleeding, missed period | hCG, TV ultrasound | Methotrexate or surgery |
| AAA (ruptured) | Shock, back/abdo pain, pulsatile mass | Bedside US, CT angio | Resuscitation + vascular surgery |
🧾 Additional Diagnostic Pearls
- 📉 Silent abdomen + rigidity → peritonitis → surgical emergency
- 🧪 Amylase 3× ULN → pancreatitis (but can rise in perforation, ectopic, DKA)
- 📍 Pain radiation clues:
- Shoulder → diaphragmatic irritation
- Back → AAA or pancreatitis
- Periumbilical → appendicitis (early)
- 🚺 All women of child-bearing age → pregnancy test mandatory
🧰 Investigations
- Bloods: FBC, U&E, CRP, LFTs, Ca, glucose, amylase/lipase, group & save
- Urine dip ± culture; urine pregnancy test
- ECG – exclude ACS
- Imaging: AXR (limited), CXR (free air, pneumonia), CT abdo (most useful), USS (biliary/gyne)
- Blood cultures if sepsis suspected
- Special: CT angiography (mesenteric ischaemia), porphobilinogen (acute porphyria)
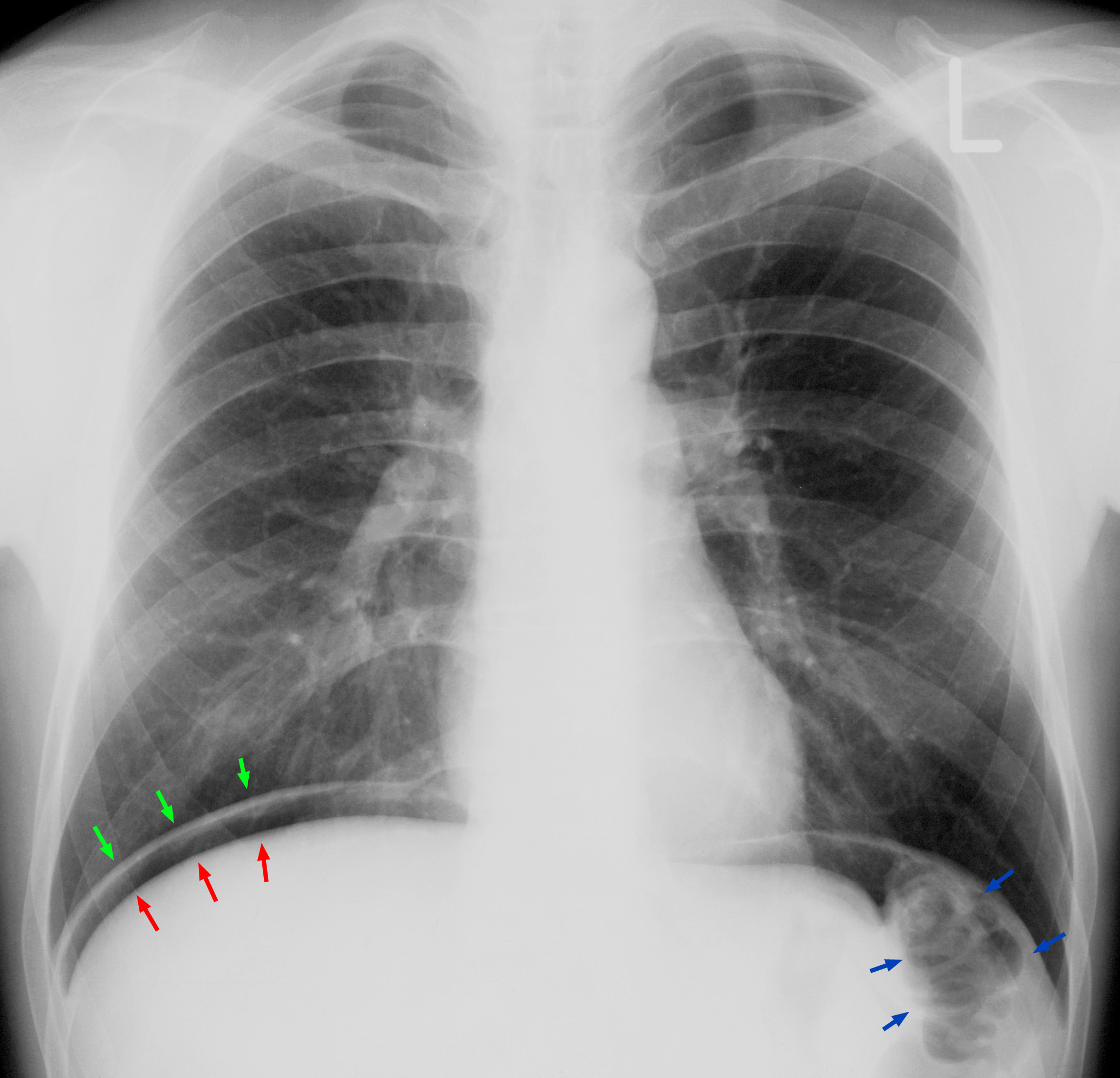
🫁 Causes of Free Sub-diaphragmatic Gas on AXR
- Perforated viscus (peptic ulcer, diverticulitis, appendix)
- Gas-forming infection
- Iatrogenic (post-laparoscopy)
- Pleuroperitoneal fistula
 ⚡ Acute Management – Principles
⚡ Acute Management – Principles
- Stabilise → ABC, O2, IV access, fluids, catheter, NG tube if obstruction
- 3L/day crystalloids minimum in pancreatitis/obstruction
- Correct electrolytes, insulin infusion if DKA
- Early antibiotics if sepsis or perforation suspected
- Urgent senior surgical review
- CT abdo for diagnosis, laparotomy if peritonitis/rupture
- DVT prophylaxis unless contraindicated
🔪 Surgical Management
- Do not delay surgery except for resuscitation
- Broad-spectrum IV antibiotics (e.g. Tazocin ± Gentamicin ± Metronidazole)
- Remove infarcted/perforated tissue
- Repair perforations, drain abscesses, lavage peritoneum
- Massive haemorrhage protocol if bleeding