Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |ECG-QT interval |Brugada Syndrome |Long QT syndrome (LQTS) Acquired |Long QT syndrome (LQTS) Congenital |Torsades de Pointes |Ventricular Fibrillation |Ventricular Tachycardia |Resuscitation - Adult Tachycardia Algorithm |Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD)
⚡ Sudden cardiac death (SCD) refers to an unexpected death caused by an abrupt loss of heart function. While rare in the young, it is devastating and often highly publicised. In older adults 👴, SCD is usually linked to coronary artery disease (CAD), whereas in younger people 👦👩🦱 it is more commonly due to cardiomyopathies or inherited ion-channelopathies.
📌 About
- 👨🦱 SCD is significantly more common in young males.
- 🏃♂️ College athletes face a 2–3× higher incidence, often due to hidden structural heart disease like arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
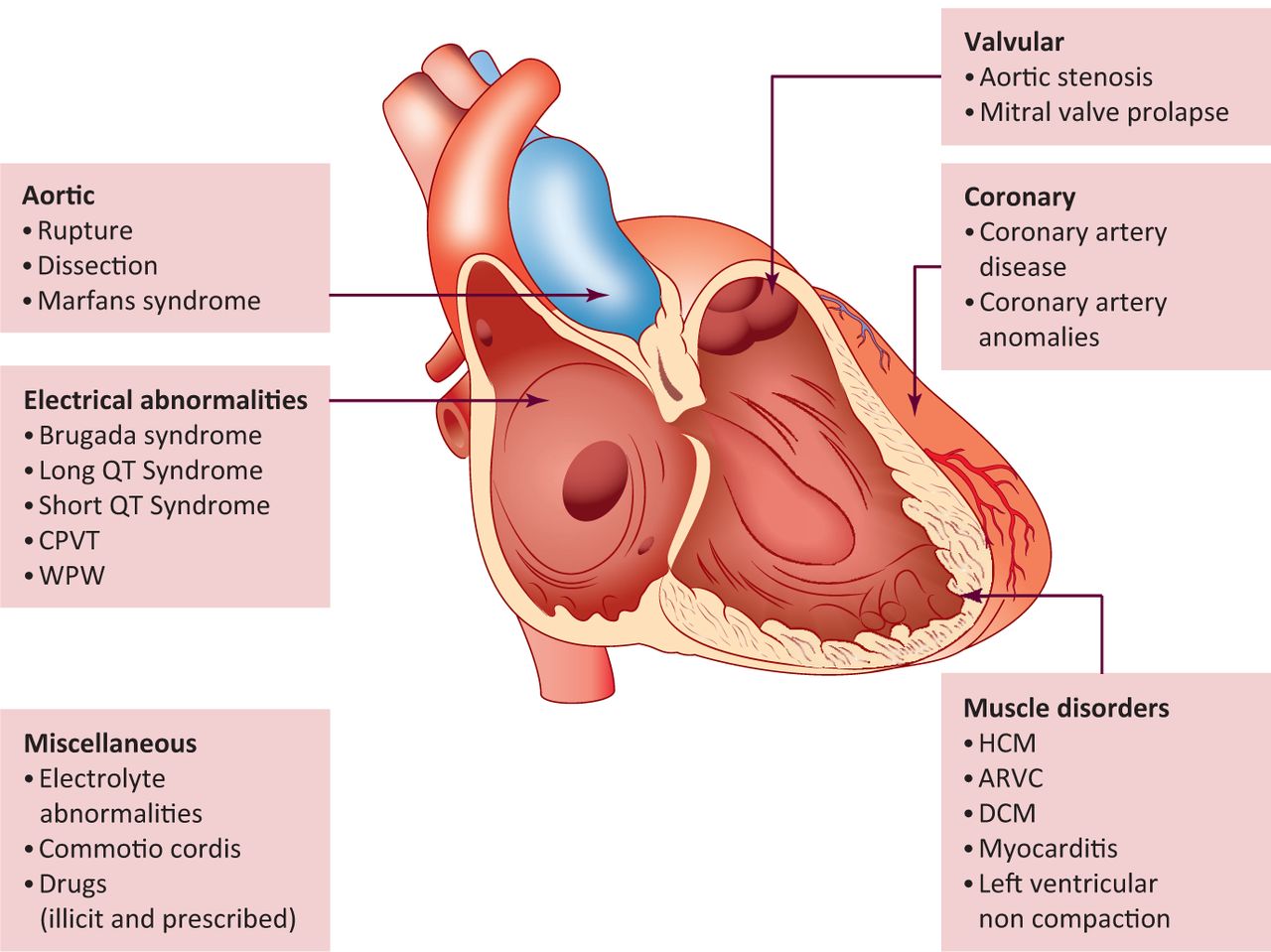
🧬 Heritable Causes
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM): Prevalence ~1 in 500; a leading cause of athletic SCD.
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC): Fibrofatty infiltration of the RV myocardium → ventricular arrhythmias.
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Ventricular dilation + impaired contraction.
- Left Ventricular Non-Compaction: Excess trabeculae → impaired systolic/diastolic function.
- Heritable Channelopathies:
- ⏱️ Long QT Syndrome (LQTS): ~1 in 2,000; predisposes to torsades de pointes.
- ⚡ Short QT Syndrome: Rare, linked with malignant arrhythmias.
- 🔥 Brugada Syndrome: Characteristic ECG with risk of VF arrest.
- 🏋️ Catecholaminergic Polymorphic VT (CPVT): Exercise or stress-triggered arrhythmias.
🫀 Structural Congenital Heart Disease (CHD)
- Combination of scarring, hypertrophy, and fibrosis predisposes to arrhythmias even after corrective surgery.
- Tetralogy of Fallot: Classic example, with ongoing SCD risk (0.1–0.2% per year post-repair).
🩺 Structurally Normal Heart (but electrical risk)
- 🔥 Brugada Syndrome: ST elevation V1–V3, VF risk.
- ⏱️ Congenital LQTS: Prolonged QTc → torsades risk.
- 💊 Acquired LQTS: Drugs/electrolyte imbalance.
- ⚡ Pre-Excitation Syndromes (e.g., WPW): AF with rapid conduction → VF risk.
- 🏏 Commotio Cordis: Chest trauma during vulnerable repolarisation phase → VF arrest.
- 😰 Catecholamine-Induced VT: Stress or exertion triggers malignant arrhythmia.
❤️ Structurally Abnormal Heart
- Ischaemic Heart Disease (IHD): 🫀 ACS or MI precipitating VF/VT.
- ARVC / ARVD: Fibrofatty replacement of RV → malignant arrhythmias.
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Thick walls, arrhythmia-prone myocardium.
- Aortic Stenosis: Severe LV outflow obstruction → exertional syncope, arrhythmia risk.
🧾 Causes of Sudden Cardiac Death
💡 SCD is not always purely cardiac — non-cardiac triggers exist too.
| Category | Cause | Clinical Details | Diagnostic Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🫁 Noncardiac | 🧠 CNS Hemorrhage | Sudden neuro decline → cardiac arrest | CT/MRI brain |
| 🫁 Massive Pulmonary Embolus | Right heart strain & collapse | CT-PA, D-dimer | |
| 💊 Drug Overdose | Cardiotoxicity/CNS depression | Toxicology screen | |
| 🌬️ Severe Lung Disease (Hypoxia) | Respiratory failure → arrest | ABG, CXR, sats | |
| 🩸 Aortic Dissection | Acute chest/back pain → collapse | CT angiogram | |
| ❤️ Cardiac | ⚡ Ventricular Fibrillation | Chaotic rhythm → immediate collapse | ECG, defibrillation |
| 🫀 Myocardial Ischaemia | Reduced coronary flow → arrhythmia | ECG, troponins | |
| ⏱️ Long QT Syndrome | QT prolongation → torsades | ECG, genetics | |
| ⚡ Brugada Syndrome | ST elevation V1–V3 → VF risk | ECG ± sodium channel blocker challenge | |
| 🏋️ Ventricular Tachycardia | Rapid broad-complex VT → collapse | ECG, EPS | |
| 🐢 Bradyarrhythmias | Sinus pauses, AV block → syncope/arrest | ECG, Holter | |
| 🔒 Aortic Stenosis | LV outflow obstruction → exertional collapse | Echocardiogram | |
| 🩸 Pericardial Tamponade | Fluid compressing heart | Echo, pericardiocentesis | |
| 🦠 Endocarditis Complications | Valve destruction/emboli → sudden arrest | Echo, cultures | |
| 💔 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy | Arrhythmia or LVOT obstruction | Echo, MRI, genetics | |
| 🩹 Kawasaki Arteritis | Coronary aneurysm rupture/occlusion | Echo, angiography |
🔍 Investigations
- 📈 ECG: Key screening tool for LQTS, WPW, HCM, Brugada.
- 👩⚕️ Clinical History & Exam: Syncope, family history, exertional symptoms.
- 🫀 Echocardiography: Structure & function — cardiomyopathies, valve disease.
📊 ECG Findings Raising SCD Risk
- ⏱️ QTc >450ms (men), >470ms (women).
- ⬇️ T-wave inversion, prolonged QRS, LBBB.
- ⚡ Non-sustained VT episodes on Holter.
- 💔 Poor LV function (echo, MRI).
🛠️ Management
- ICD (Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator): 💡 Life-saving in high-risk patients, but consider device-related complications in younger patients.
- Device Complications: ⚠️ Inappropriate shocks, lead malfunctions, anatomical challenges in children/young adults.