Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Peripheral neuropathy
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Note 📝: In the UK and US, the most common causes of peripheral neuropathy are diabetes and alcohol abuse 🍺. Worldwide 🌍, leprosy 🧑⚕️ remains a significant cause.
🔎 About Peripheral Neuropathy
- Also see “Length-Dependent Polyneuropathy” for further detail.
- Peripheral neuropathy = disease of peripheral nerves, usually secondary to systemic or primary neurological conditions.
- Clinical patterns vary: may be symmetrical or patchy, distal or proximal, and affect motor, sensory, or autonomic function.
⚙️ Aetiology
- Peripheral nerves have two major fibre types:
- Small fibres 🔥: pain, temperature, autonomic function.
- Large fibres 🎻: motor strength, vibration, proprioception.
🧩 Different Forms of Peripheral Neuropathy
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Wallerian Degeneration | After nerve transection, distal axon + myelin degenerate; regeneration proceeds proximally → distally (often incomplete). |
| Axonal Degeneration | “Dying back” pattern; toxins, diabetes, alcohol, nutritional deficiencies common culprits. |
| Demyelination | Loss of myelin with preserved axons; e.g. Guillain–Barré, CIDP. |
| Neuronal Cell Body Disease | Anterior horn cell involvement (e.g. polio, MND, paraneoplastic). |
| Dorsal Root Ganglionopathy | Affects sensory ganglia; causes patchy sensory loss (e.g. paraneoplastic, Sjögren’s). |
🧭 Patterns of Peripheral Neuropathy
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
| Polyneuropathy 🧦 | Distal, symmetrical “glove and stocking” loss; diabetes, alcohol, B12 deficiency, Lyme disease. |
| Mononeuropathy 🔒 | Single nerve lesion (e.g. carpal tunnel, ulnar palsy, diabetic entrapments). |
| Mononeuritis Multiplex 🌿 | Asymmetric multi-nerve involvement; think vasculitis. |
| Autonomic Neuropathy ⚡ | Postural hypotension, bowel/bladder issues; causes include diabetes, amyloidosis, toxins. |
| Abrupt-Onset Neuropathy 🚨 | Ischaemic; PAN, RA, HIV-related. |
| Cranial Nerve Involvement 👁️ | E.g. bilateral facial palsy in diabetes, Lyme, sarcoid, GBS. |
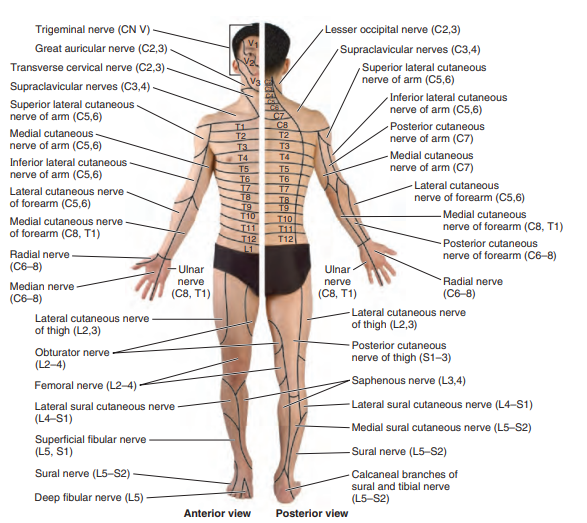
🩺 Common Causes
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Diabetes Mellitus | Symmetrical distal sensorimotor + autonomic neuropathy (most common UK cause). |
| Alcohol Abuse 🍺 | Painful, distal symmetric sensorimotor neuropathy; worsened by vitamin deficiencies. |
| B12 Deficiency 🍊 | Loss of proprioception, ataxia, brisk reflexes (mixed neuropathy + myelopathy). |
| Uraemia 💧 | Common in CKD or dialysis patients. |
| Autoimmune (RA, SLE) | Can cause distal sensory-motor neuropathy. |
| Paraneoplastic 🧬 | Often sensory; think lymphoma, lung cancer. |
| Vasculitis | Mononeuritis multiplex; painful, abrupt onset. |
| Chemotherapy 💊 | Platinum agents, vinca alkaloids; distal symmetrical neuropathy. |
| Guillain–Barré (GBS) | Acute demyelinating polyneuropathy with autonomic features; albuminocytologic dissociation. |
| CIDP | Chronic demyelinating sensorimotor neuropathy; relapsing/progressive course. |
| Hereditary (e.g. CMT) | Distal weakness, pes cavus, family history. |
| Leprosy 🦠 | Worldwide leading cause; thickened nerves, anaesthetic skin patches. |
🧾 Clinical Features
- Sensory: Paraesthesia, burning pain, allodynia, proprioceptive loss → ataxia.
- Motor: Distal weakness, areflexia, foot drop, “high-stepping” gait.
- Autonomic: Postural hypotension, bowel/bladder dysfunction, erectile difficulties.
- Hereditary Clues: Pes cavus, hammer toes.
- Nerve Thickening: Rare; in leprosy, CIDP, CMT.
📈 Rate of Onset
- Days: GBS, vasculitis.
- Weeks: CIDP.
- Months–Years: Diabetes, alcohol, hereditary neuropathies.
🧭 Diagnostic Clues
- Speed of onset (acute vs chronic).
- Systemic history (diabetes, alcohol, autoimmune disease).
- Cranial/autonomic involvement → red flag.
- Distribution: small fibre vs large fibre.
- Family history → hereditary cause.
🔬 Investigations
- First-line: FBC, ESR, CRP, U&E, LFTs, glucose/HbA1c, B12, folate, TFTs.
- Autoimmune: ANA, dsDNA, ENA, ANCA.
- Infectious: HIV, hepatitis serology, CXR (TB/sarcoid).
- NCS/EMG: To classify as axonal vs demyelinating, motor vs sensory.
- Selective: CSF (GBS/CIDP), ACE (sarcoid), genetic testing (CMT), nerve biopsy if unclear.
💊 Management
- Always treat the underlying cause (e.g. glycaemic control, alcohol cessation, B12 replacement).
- Neuropathic pain: duloxetine, gabapentin, pregabalin.
- Supportive: physiotherapy, orthotics, podiatry, lifestyle adjustments.
- Immune-mediated: IVIG, steroids, plasma exchange (GBS, CIDP).
Cases — Peripheral Neuropathy
- Case 1 — Diabetic Neuropathy (Metabolic): A 62-year-old man with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes reports numbness and burning pain in both feet, worse at night. Exam: stocking distribution sensory loss, reduced ankle reflexes, preserved power. Diagnosis: Distal symmetric sensory neuropathy due to diabetes. Management: Optimise glycaemic control; neuropathic pain agents (duloxetine, pregabalin); podiatry care to prevent ulcers.
- Case 2 — Alcoholic Neuropathy (Toxic + Nutritional): A 55-year-old man with long-standing alcohol excess presents with tingling and weakness in his legs. Exam: distal wasting, areflexia, sensory loss to vibration. Diagnosis: Peripheral neuropathy due to alcohol toxicity and thiamine deficiency. Management: Abstinence from alcohol, thiamine supplementation, physiotherapy.
- Case 3 — Vitamin B12 Deficiency (Nutritional): A 45-year-old vegan develops progressive numbness in feet and unsteady gait. Exam: reduced vibration sense, positive Romberg, brisk reflexes (subacute combined degeneration). Diagnosis: Peripheral neuropathy due to vitamin B12 deficiency. Management: Parenteral vitamin B12 replacement; treat cause (e.g., pernicious anaemia).
- Case 4 — Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease (Hereditary): A 19-year-old man has progressive foot deformities and distal weakness. Exam: pes cavus, foot drop, absent ankle reflexes, glove-and-stocking sensory loss. Family history of similar symptoms. Diagnosis: Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy (Charcot–Marie–Tooth). Management: Supportive: physiotherapy, orthotics, genetic counselling.
- Case 5 — Guillain–Barré Syndrome (Immune-Mediated, Acute): A 33-year-old man develops ascending weakness 2 weeks after a diarrhoeal illness. Exam: areflexia, bilateral foot drop, and distal paraesthesia. Diagnosis: Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (GBS). Management: Admit for monitoring; IV immunoglobulin or plasma exchange; respiratory support if vital capacity drops.
Teaching Commentary 🧠
Peripheral neuropathies can be classified by pattern (sensory, motor, sensorimotor), time course (acute vs chronic), and cause (metabolic, toxic, nutritional, hereditary, immune, infectious). - Diabetes = most common cause worldwide. - Alcohol + nutritional deficiencies common in Western settings. - Vitamin B12 deficiency gives mixed neuropathy + myelopathy. - Charcot–Marie–Tooth = hereditary with pes cavus. - GBS/CIDP = acute or chronic demyelinating immune neuropathies. Approach: history, examination (distribution, symmetry, reflexes), then confirm with nerve conduction studies, bloods, and targeted tests. Management is always cause-specific + supportive.