Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Necrotising fasciitis
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Cellulitis |Pyoderma gangrenosum |Pemphigus Vulgaris |Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis |Stevens-Johnson Syndrome |Necrotising fasciitis |Gas Gangrene (Clostridium perfringens) |Purpura Fulminans |Severe burns |Anatomy of Skin
💡 Teaching Pearl: Necrotising fasciitis is both a medical and surgical emergency. Immediate diagnosis and treatment save lives. Delay in surgery = higher mortality. Variants: Meleney’s gangrene, Fournier’s gangrene.
| ⚠️ Necrotising Fasciitis – Key Emergency Features |
|---|
|
Necrotizing fasciitis is a medical and surgical emergency that requires immediate attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial, as delays can significantly increase mortality rates. This severe infection often necessitates extensive surgery, reconstruction, and, in some cases, amputation. Meleney’s synergistic gangrene and Fournier’s gangrene are variants of a similar disease process.
About
- Definition: Necrotizing fasciitis is a deep infection characterized by necrosis and damage to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
- Pathophysiology: The infection can traverse the usual fascial layers that typically limit the spread of infection.
- Etiology: Caused by Gram-negative or Gram-positive anaerobic bacteria.
- Entry Point: May originate from a small wound at the skin surface.
Risks
- Individuals with diabetes mellitus.
- People who inject drugs.
- Patients with haematological malignancies.
- Smoking; penetrating trauma
- Pressure sores; immunosuppression
- Perineal infection (perianal abscess, Bartholin’s cysts)
- Skin damage/infection (abrasions, bites, boils)
Microbiology: Polymicrobial and Mixed
Necrotising fasciitis results from synergistic, polymicrobial infection; most commonly a streptococcal species (Group A -haemolytic) in combination with Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Proteus, Bacteroides or Clostridia
- Group A Beta-Haemolytic Streptococci (GAS): A major cause, often referred to as "flesh-eating disease."
- Staphylococcus aureus (including MRSA): Commonly involved in mixed infections.
- Aeromonas hydrophila: Predominantly seen in tropical regions.
- Vibrio vulnificus: Associated with seawater exposure in tropical climates.
- Fungal Infections: Can occur, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Clostridium Species: Associated with gas gangrene and gas formation in tissues.
Classification
- Type 1: Mixed Infection
- Combination of Enterobacteriaceae and anaerobes.
- Common in immunocompromised patients, diabetics, and post-surgical patients.
- Type 2: Streptococcal Infection
- Caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (Lancefield Group A).
- Produces a superantigen that activates T cells and macrophages, leading to extensive tissue damage.
- Known as the "flesh-eating disease."
- Type 3: Clostridial Myonecrosis (Gas Gangrene)
- Related to trauma or surgery.
- Caused by Clostridium perfringens.
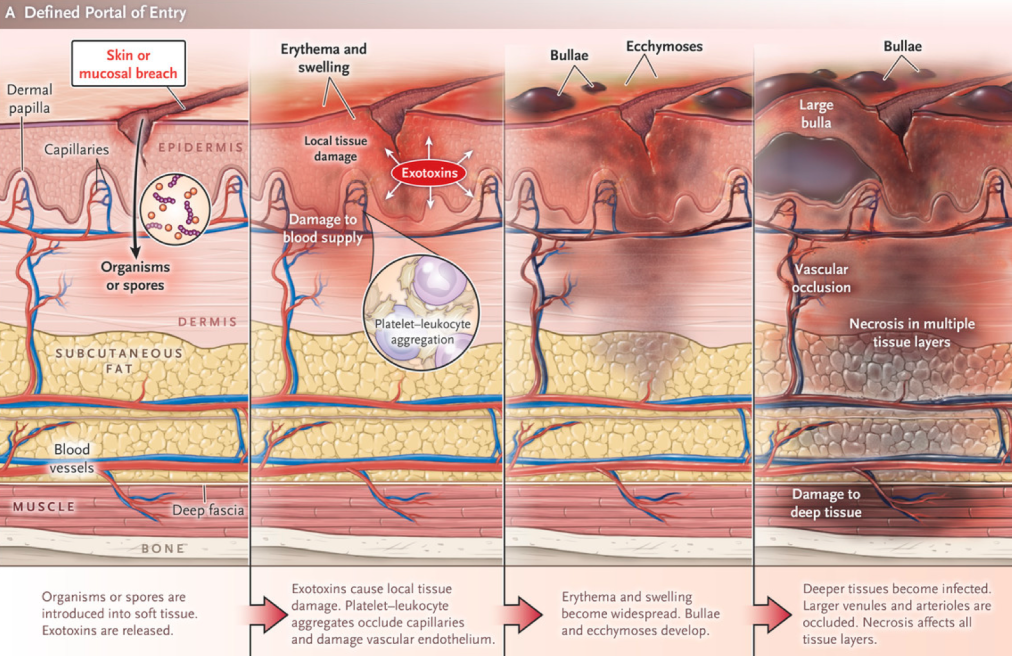
Clinical Features
Oedema stretching beyond visible skin erythema; a woody-hard texture to the subcutaneous tissues; an inability to distinguish fascial planes and muscle groups on palpation; disproportionate pain in relation to the affected area, with associated skin vesicles and soft tissue crepitus
- Severe Pain and Swelling: Intense pain and rapid swelling in the affected area.
- Systemic Symptoms: Severe systemic inflammatory response, including fever and tachycardia.
- Anaesthetic Center: The center of the lesion may be anaesthetic due to nerve damage.
- Crepitus: Presence of gas beneath the skin, detectable as crepitus.
- Multisystem Failure: Advanced cases can lead to multi-organ dysfunction and failure.
Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) Score
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP): >150 mg/L or 15 mg/dL (+4)
- White Cell Count (WCC): 15-25 (+1), >25 (+2)
- Sodium (Na): <135 mmol/L (+2)
- Creatinine: >141 μmol/L or 1.6 mg/dL (+2)
- Glucose: >180 mg/dL or 100 mmol/L (+1)
- Interpretation:
- A LRINEC score of 6 or more suggests necrotizing fasciitis.
- A LRINEC score below 6 does not rule out the diagnosis.
- Note: Use with caution as the LRINEC Score has performed poorly in external validation. MDCalc - LRINEC Score
Differential Diagnosis
- Toxic Shock Syndrome.
- Mucormycosis Infection.
Investigations
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Elevated WCC.
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP): Significantly elevated.
- Urea and Electrolytes (U&E): May reveal acute kidney injury (AKI).
- Calcium Levels: Hypocalcemia may be present.
- Imaging: MRI or CT scans can assess the extent of soft tissue involvement and presence of gas.
Management
- Immediate Support:
- Follow the ABC protocol (Airway, Breathing, Circulation).
- Provide supplemental oxygen and support ventilation if necessary.
- Administer intravenous fluids to maintain blood pressure and organ perfusion.
- Consider hyperbaric oxygen therapy, especially in mixed infections if available.
- Surgical Intervention:
Early surgical review and further debridement is advisable, together with the use vacuum-assisted dressings. Early skin grafting in selected cases may minimise protein and fluid losses
- Immediate consultation with a surgeon is crucial.
- Initiate broad-spectrum antibiotics and proceed with aggressive surgical debridement.
- If necrotizing fasciitis is suspected, perform an exploratory incision and inspection to confirm diagnosis.
- Debridement should be prompt to remove all necrotic tissue.
- Delayed surgery is associated with increased mortality rates.
- Plastic surgeons and/or on-call polytrauma consultants are preferred for initial management.
- Obtain specimens for microbiological culture and sensitivity (MC&S) and histological examination.
- Antibiotic Therapy:
- Standard Regimen: Benzyl Penicillin 1.2g IV every 4 hours plus Clindamycin 600mg IV four times daily plus Gentamicin once daily IV.
- Penicillin Allergy: Use Clindamycin 600mg IV four times daily plus Gentamicin once daily IV.
- Adjunct Therapies:
- Antibiotic stewardship to ensure appropriate use of antimicrobials.
- Monitoring and managing organ dysfunction and other systemic complications.
Prognosis
- Necrotizing fasciitis has a high mortality rate if not treated promptly.
- Early diagnosis and aggressive management significantly improve survival rates.
- Complications may include extensive tissue loss, requiring reconstructive surgery and, in severe cases, amputation.
- Long-term outcomes depend on the extent of tissue damage and the timeliness of intervention.
Conclusion
Necrotizing fasciitis is a life-threatening infection that demands immediate medical and surgical intervention. Rapid recognition, prompt antibiotic therapy, and aggressive surgical debridement are essential to improve patient outcomes and reduce mortality. Healthcare providers must maintain a high index of suspicion, especially in high-risk populations, to ensure timely diagnosis and management.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Necrotizing Fasciitis. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov
- Mayo Clinic. Necrotizing Fasciitis. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). Necrotizing Fasciitis. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- World Health Organization (WHO). Infectious Diseases. Available at: https://www.who.int
- MDCalc. LRINEC Score for Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection. Available at: https://www.mdcalc.com