Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Cardiology Examination (OSCE)
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Breast Anatomy and Examination (OSCE) |Shoulder examination(OSCE) |Testicular examination(OSCE) |Hernia Examination (OSCE) |Rectal examination (OSCE) |Liver Examination (OSCE) |Cerebellar Examination (OSCE) |Upper and Lower Limb Neurology (OSCE) |Gastroenterology Examination (OSCE) |Respiratory Examination (OSCE) |Cardiology Examination (OSCE)
🔍 A cardiac exam is an active process — always think and look for signs systematically rather than waiting for them to appear.
| 🫁 Cardiology Exam: Overall Plan |
|---|
|
💡 Exam Pearls
• Always state BP would be measured. • Add “I’d like to complete with fundoscopy, urine dip, ECG & echo.” • JVP is best seen with tangential light. • Clubbing + splinter haemorrhages + new murmur = think infective endocarditis. • Always compare both sides: pulses, auscultation areas.
🫀 Complete Cardiac Examination OSCE Guide
👉 The cardiac exam is an active process — you must think, look, and integrate findings systematically. This article combines structured steps, teaching pearls, common findings, and a rapid-revision checklist into one complete resource.
🔑 Principles
- Follow a clear sequence: Inspection → Palpation → Auscultation → Special Maneuvers → Peripheral Signs → Closure.
- Always communicate with the patient and maintain dignity.
- Finish by stating how you’d complete the exam (BP, fundoscopy, urine dipstick, ECG, echo).
- Examiner tip: Talk through your steps. If you forget to do something, verbalising still gains marks. <
1️⃣ Preparation
- 🧼 Wash hands
- 👋 Introduce yourself & confirm patient ID
- 📝 Explain exam, obtain consent
- 🛏️ Position: semi-recumbent (45°), expose chest to waist while maintaining dignity
2️⃣ General Inspection (End of Bed 👀)
- Patient: distress, breathlessness, cyanosis, pallor, cachexia
- Environment: oxygen, nebulisers, GTN spray, IV fluids, ECG leads, mobility aids
- Bedside clues: urine pot (haematuria), sputum pot, fluid balance charts
3️⃣ Hands & Arms ✋
- Inspection: clubbing, splinter haemorrhages, Osler’s nodes, Janeway lesions, tendon xanthomata
- Pulses:
- Rate & rhythm (AF → irregularly irregular)
- Character: 🐢 Slow-rising → AS
| 💧 Collapsing → AR
- Radio-radial delay → subclavian stenosis
- Radio-femoral delay → coarctation of aorta
- BP measurement (mention both arms)
4️⃣ Face & Neck 🙂 & Eyes 👁️
- Eyes: xanthelasma, corneal arcus, conjunctival pallor, Roth spots
- Mouth: cyanosis, poor dentition
- Conjunctival pallor (anaemia), central cyanosis (lips, tongue).
- Xanthelasma / corneal arcus → hyperlipidaemia.
- Malar flush → mitral stenosis. Down’s/Turner’s/Marfan’s facies (syndromic associations).
- Neck: JVP at 45°, hepatojugular reflux, carotid pulse (one side at a time), listen for bruits
Hands ✋
- Clubbing → congenital cyanotic heart disease, endocarditis.
- Splinter haemorrhages, Osler’s nodes, Janeway lesions → endocarditis.
- Nicotine staining, tendon xanthomata, arachnodactyly, joint hypermobility (Marfan/Ehlers-Danlos).
- Temperature (warm/cold), perfusion.
Pulse & Rhythm ❤️
- Rate (brady <60, tachy >100). Count for 15s or full minute if irregular.
- Rhythm: regular / irregularly irregular (AF) / regularly irregular (ectopics, Mobitz II).
- Character: collapsing (AR), slow-rising (AS), jerky (HOCM), bisferiens (mixed AR/AS).
- Compare both radials; check radiofemoral delay (coarctation).
Blood Pressure 💉
- Measure both arms if coarctation/dissection suspected.
- Pulse pressure: narrow (AS), wide (AR, thyrotoxicosis).
5️⃣ Chest Inspection 👕
- Scars: sternotomy, lateral thoracotomy, ICD/PPM bulge
- Deformities: pectus excavatum, scoliosis
- Visible pulsations
- Pacemaker scars (usually L infraclavicular).
6️⃣ Palpation 🤲
- Apex beat: site, size, character, displacement
- Heaves: RV hypertrophy
- Thrills: palpable murmurs
7️⃣ Auscultation 🎧
- Areas (use diaphragm + bell):
- 🔴 Aortic → 2nd ICS, RSB
- 🔵 Pulmonary → 2nd ICS, LSB
- 🟢 Tricuspid → 4th ICS, LSE
- 🟣 Mitral (apex) → 5th ICS, MCL
- Axilla → MR radiation
- Carotids → AS radiation (after bruit check)
- Listen for:
- S1 & S2 clarity
- Extra sounds: 💧 S3 (HF, overload), 🔔 S4 (stiff LV)
- Murmurs: systolic, diastolic, timing, radiation
- Pericardial rub: scratchy, triphasic
8️⃣ Special Maneuvers ⚡
- Valsalva → ↑ HOCM murmur
- Handgrip → ↑ MR & AR murmurs
- Left lateral decubitus → accentuates MS, S3
- Sit forward + expiration → accentuates AR
9️⃣ Peripheral Signs 👣
- Lung bases → crackles (CCF)
- Sacrum & ankles → oedema
- Legs → saphenous vein harvest scars with sternotomy scar for CABG, varicosities
- Face → malar flush (MS), cyanosis
🔟 Closure 🙏
- Thank patient, assist redressing
- Wash hands again
- Present findings
- State further steps: BP (both arms), fundoscopy, urine dipstick, ECG, echo
- Patient: distress, breathlessness, cyanosis, pallor, cachexia
- Environment: oxygen, nebulisers, GTN spray, IV fluids, ECG leads, mobility aids
- Bedside clues: urine pot (haematuria), sputum pot, fluid balance charts
3️⃣ Hands & Arms ✋
- Inspection: clubbing, splinter haemorrhages, Osler’s nodes, Janeway lesions, tendon xanthomata
- Pulses:
- Rate & rhythm (AF → irregularly irregular)
- Character: 🐢 Slow-rising → AS
| 💧 Collapsing → AR
- Radio-radial delay → subclavian stenosis
- Radio-femoral delay → coarctation of aorta
- BP measurement (mention both arms)
4️⃣ Face & Neck 🙂 & Eyes 👁️
- Eyes: xanthelasma, corneal arcus, conjunctival pallor, Roth spots
- Mouth: cyanosis, poor dentition
- Conjunctival pallor (anaemia), central cyanosis (lips, tongue).
- Xanthelasma / corneal arcus → hyperlipidaemia.
- Malar flush → mitral stenosis. Down’s/Turner’s/Marfan’s facies (syndromic associations).
- Neck: JVP at 45°, hepatojugular reflux, carotid pulse (one side at a time), listen for bruits
Hands ✋
- Clubbing → congenital cyanotic heart disease, endocarditis.
- Splinter haemorrhages, Osler’s nodes, Janeway lesions → endocarditis.
- Nicotine staining, tendon xanthomata, arachnodactyly, joint hypermobility (Marfan/Ehlers-Danlos).
- Temperature (warm/cold), perfusion.
Pulse & Rhythm ❤️
- Rate (brady <60, tachy >100). Count for 15s or full minute if irregular.
- Rhythm: regular / irregularly irregular (AF) / regularly irregular (ectopics, Mobitz II).
- Character: collapsing (AR), slow-rising (AS), jerky (HOCM), bisferiens (mixed AR/AS).
- Compare both radials; check radiofemoral delay (coarctation).
Blood Pressure 💉
- Measure both arms if coarctation/dissection suspected.
- Pulse pressure: narrow (AS), wide (AR, thyrotoxicosis).
5️⃣ Chest Inspection 👕
- Scars: sternotomy, lateral thoracotomy, ICD/PPM bulge
- Deformities: pectus excavatum, scoliosis
- Visible pulsations
- Pacemaker scars (usually L infraclavicular).
6️⃣ Palpation 🤲
- Apex beat: site, size, character, displacement
- Heaves: RV hypertrophy
- Thrills: palpable murmurs
7️⃣ Auscultation 🎧
- Areas (use diaphragm + bell):
- 🔴 Aortic → 2nd ICS, RSB
- 🔵 Pulmonary → 2nd ICS, LSB
- 🟢 Tricuspid → 4th ICS, LSE
- 🟣 Mitral (apex) → 5th ICS, MCL
- Axilla → MR radiation
- Carotids → AS radiation (after bruit check)
- Listen for:
- S1 & S2 clarity
- Extra sounds: 💧 S3 (HF, overload), 🔔 S4 (stiff LV)
- Murmurs: systolic, diastolic, timing, radiation
- Pericardial rub: scratchy, triphasic

8️⃣ Special Maneuvers ⚡
- Valsalva → ↑ HOCM murmur
- Handgrip → ↑ MR & AR murmurs
- Left lateral decubitus → accentuates MS, S3
- Sit forward + expiration → accentuates AR
9️⃣ Peripheral Signs 👣
- Lung bases → crackles (CCF)
- Sacrum & ankles → oedema
- Legs → saphenous vein harvest scars with sternotomy scar for CABG, varicosities
- Face → malar flush (MS), cyanosis
🔟 Closure 🙏
- Thank patient, assist redressing
- Wash hands again
- Present findings
- State further steps: BP (both arms), fundoscopy, urine dipstick, ECG, echo
- Rate & rhythm (AF → irregularly irregular)
- Character: 🐢 Slow-rising → AS | 💧 Collapsing → AR
- Radio-radial delay → subclavian stenosis
- Radio-femoral delay → coarctation of aorta
- Eyes: xanthelasma, corneal arcus, conjunctival pallor, Roth spots
- Mouth: cyanosis, poor dentition
- Conjunctival pallor (anaemia), central cyanosis (lips, tongue).
- Xanthelasma / corneal arcus → hyperlipidaemia.
- Malar flush → mitral stenosis. Down’s/Turner’s/Marfan’s facies (syndromic associations).
- Neck: JVP at 45°, hepatojugular reflux, carotid pulse (one side at a time), listen for bruits
Hands ✋
- Clubbing → congenital cyanotic heart disease, endocarditis.
- Splinter haemorrhages, Osler’s nodes, Janeway lesions → endocarditis.
- Nicotine staining, tendon xanthomata, arachnodactyly, joint hypermobility (Marfan/Ehlers-Danlos).
- Temperature (warm/cold), perfusion.
Pulse & Rhythm ❤️
- Rate (brady <60, tachy >100). Count for 15s or full minute if irregular.
- Rhythm: regular / irregularly irregular (AF) / regularly irregular (ectopics, Mobitz II).
- Character: collapsing (AR), slow-rising (AS), jerky (HOCM), bisferiens (mixed AR/AS).
- Compare both radials; check radiofemoral delay (coarctation).
Blood Pressure 💉
- Measure both arms if coarctation/dissection suspected.
- Pulse pressure: narrow (AS), wide (AR, thyrotoxicosis).
5️⃣ Chest Inspection 👕
- Scars: sternotomy, lateral thoracotomy, ICD/PPM bulge
- Deformities: pectus excavatum, scoliosis
- Visible pulsations
- Pacemaker scars (usually L infraclavicular).
6️⃣ Palpation 🤲
- Apex beat: site, size, character, displacement
- Heaves: RV hypertrophy
- Thrills: palpable murmurs
7️⃣ Auscultation 🎧
- Areas (use diaphragm + bell):
- 🔴 Aortic → 2nd ICS, RSB
- 🔵 Pulmonary → 2nd ICS, LSB
- 🟢 Tricuspid → 4th ICS, LSE
- 🟣 Mitral (apex) → 5th ICS, MCL
- Axilla → MR radiation
- Carotids → AS radiation (after bruit check)
- Listen for:
- S1 & S2 clarity
- Extra sounds: 💧 S3 (HF, overload), 🔔 S4 (stiff LV)
- Murmurs: systolic, diastolic, timing, radiation
- Pericardial rub: scratchy, triphasic

8️⃣ Special Maneuvers ⚡
- Valsalva → ↑ HOCM murmur
- Handgrip → ↑ MR & AR murmurs
- Left lateral decubitus → accentuates MS, S3
- Sit forward + expiration → accentuates AR
9️⃣ Peripheral Signs 👣
- Lung bases → crackles (CCF)
- Sacrum & ankles → oedema
- Legs → saphenous vein harvest scars with sternotomy scar for CABG, varicosities
- Face → malar flush (MS), cyanosis
🔟 Closure 🙏
- Thank patient, assist redressing
- Wash hands again
- Present findings
- State further steps: BP (both arms), fundoscopy, urine dipstick, ECG, echo
- Apex beat: site, size, character, displacement
- Heaves: RV hypertrophy
- Thrills: palpable murmurs
7️⃣ Auscultation 🎧
- Areas (use diaphragm + bell):
- 🔴 Aortic → 2nd ICS, RSB
- 🔵 Pulmonary → 2nd ICS, LSB
- 🟢 Tricuspid → 4th ICS, LSE
- 🟣 Mitral (apex) → 5th ICS, MCL
- Axilla → MR radiation
- Carotids → AS radiation (after bruit check)
- Listen for:
- S1 & S2 clarity
- Extra sounds: 💧 S3 (HF, overload), 🔔 S4 (stiff LV)
- Murmurs: systolic, diastolic, timing, radiation
- Pericardial rub: scratchy, triphasic

8️⃣ Special Maneuvers ⚡
- Valsalva → ↑ HOCM murmur
- Handgrip → ↑ MR & AR murmurs
- Left lateral decubitus → accentuates MS, S3
- Sit forward + expiration → accentuates AR
9️⃣ Peripheral Signs 👣
- Lung bases → crackles (CCF)
- Sacrum & ankles → oedema
- Legs → saphenous vein harvest scars with sternotomy scar for CABG, varicosities
- Face → malar flush (MS), cyanosis
🔟 Closure 🙏
- Thank patient, assist redressing
- Wash hands again
- Present findings
- State further steps: BP (both arms), fundoscopy, urine dipstick, ECG, echo
- 🔴 Aortic → 2nd ICS, RSB
- 🔵 Pulmonary → 2nd ICS, LSB
- 🟢 Tricuspid → 4th ICS, LSE
- 🟣 Mitral (apex) → 5th ICS, MCL
- Axilla → MR radiation
- Carotids → AS radiation (after bruit check)
- S1 & S2 clarity
- Extra sounds: 💧 S3 (HF, overload), 🔔 S4 (stiff LV)
- Murmurs: systolic, diastolic, timing, radiation
- Pericardial rub: scratchy, triphasic
- Valsalva → ↑ HOCM murmur
- Handgrip → ↑ MR & AR murmurs
- Left lateral decubitus → accentuates MS, S3
- Sit forward + expiration → accentuates AR
9️⃣ Peripheral Signs 👣
- Lung bases → crackles (CCF)
- Sacrum & ankles → oedema
- Legs → saphenous vein harvest scars with sternotomy scar for CABG, varicosities
- Face → malar flush (MS), cyanosis
🔟 Closure 🙏
- Thank patient, assist redressing
- Wash hands again
- Present findings
- State further steps: BP (both arms), fundoscopy, urine dipstick, ECG, echo
- Thank patient, assist redressing
- Wash hands again
- Present findings
- State further steps: BP (both arms), fundoscopy, urine dipstick, ECG, echo
Present your findings clearly: “This patient has an ejection systolic murmur loudest in the aortic area, radiating to the carotids, with a slow-rising pulse and narrow pulse pressure — consistent with severe aortic stenosis.” Examiner tip: Even if unsure, structure + reasoning = marks.
💡 Teaching Pearls
• State missing steps you’d add (ECG, echo, fundoscopy, urine dip). • JVP is measured in cm above the sternal angle. • Always comment on scars and environment clues. • Clubbing + splinter haemorrhages + new murmur → think endocarditis. • A collapsing pulse is best felt by raising the arm above the head. • In OSCEs: “I’d like to complete the exam with BP, fundoscopy, urine dip, ECG, echo.” = ✅ marks.
📊 Common Cardiac Examination Findings (Master Table)
| Finding | Description | Technique | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🫀 Normal S1 & S2 | Crisp closure of AV & semilunar valves | Auscultation at all standard areas | Normal cardiac function |
| 🔀 Physiological split S2 | Inspiration delays P2 closure | Pulmonary area during inspiration/expiration | Normal; fixed split → ASD |
| 🎵 Systolic murmur | Harsh/blowing/ musical during systole | Auscultate; use maneuvers | Aortic stenosis, Mitral regurgitation, VSD |
| 🎶 Diastolic murmur | Low-pitched rumble | Bell at apex in LLDP | Mitral stenosis, Aortic regurgitation |
| 💧 S3 | Early diastolic sound during rapid filling | Bell at apex in LLDP | Heart failure, volume overload |
| 🔔 S4 | Late diastolic sound before S1 | Bell at apex (supine) | Stiff LV (HTN, IHD) |
| 🔊 Pericardial rub | Scratchy, triphasic sound | Lean forward, breath held | Acute pericarditis |
| ⚙️ Continuous murmur | “Machinery” quality throughout cycle | L infraclavicular area | Patent ductus arteriosus |
| ✋ Collapsing pulse | Bounding upstroke, rapid collapse | Palpate radial while raising arm | Aortic regurgitation, PDA, hyperdynamic states |
| 🐢 Slow-rising pulse | Gradual carotid upstroke | Palpate carotid pulse | Aortic stenosis |
Additional Information
🫀 Cardiovascular Examination: High-Yield Signs, Pulses & Murmurs
Mentor’s tip: anchor your exam to a structured sequence (look ➝ feel ➝ listen ➝ manoeuvres). Correlate each finding with haemodynamics and a differential. Small extra manoeuvres (e.g., handgrip, leaning forward) massively increase diagnostic yield.
👀 General Findings & Likely Causes
| Finding | Appearance | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Central/Peripheral Cyanosis 💙 | Bluish lips/tongue (central) or nailbeds (peripheral) | Congenital cyanotic heart disease, severe LV failure, pulmonary HTN, hypoxaemia, shunts (Eisenmenger) |
| Clubbing ☁️ | Loss of nailfold angle; spongy nailbed | Infective endocarditis, cyanotic CHD; (non-cardiac: bronchiectasis, lung Ca, IBD) |
| Splinter haemorrhages 🔴 | Longitudinal nail bed streaks | Infective endocarditis, vasculitis, trauma |
| Janeway lesions / Osler nodes / Roth spots 🦠 | Painless palms/soles macules; painful pulp nodules; retinal haemorrhages | Infective endocarditis |
| Jaundice 🟡 | Yellow sclerae/skin | Congestive hepatopathy (RHF), haemolysis (IE) |
| Peripheral oedema 🦶 | Pitting ankle/leg swelling | RHF, venous insufficiency, nephrotic syndrome; drugs (CCBs) |
| JVP ↑ / Distended neck veins 🪜 | Raised venous column, abnormal waves | RHF, TR (giant v), tamponade (y descent blunted), constrictive pericarditis (prominent y), SVC obstruction |
| Hepatomegaly ± Ascites 🫁 | Liver edge below costal margin; shifting dullness | RHF, TR, constriction; “cardiac cirrhosis” |
| Cachexia ⚖️ | Weight loss, muscle wasting | Advanced HF, chronic IE, malignancy |
| Palmar erythema ✋ | Red palms | Chronic liver disease (from HF), IE, pregnancy, thyrotoxicosis |
🖐️ Pulses: What They Tell You
| Pulse | Characteristics | Associated Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | Regular rate & amplitude | Physiological |
| Bounding / “Water-hammer” 🚰 | Collapsing, wide pulse pressure | Aortic regurgitation (Corrigan), PDA, thyrotoxicosis, fever, pregnancy |
| Thready 🪡 | Weak, rapid | Shock, severe hypovolaemia, advanced HF |
| Pulsus paradoxus 🎭 | SBP drop >10 mmHg on inspiration | Tamponade, severe asthma/COPD, constrictive pericarditis |
| Pulsus alternans ↕️ | Alternating strong/weak beats | Severe LV systolic failure |
| Bisferiens 〰️ | Two systolic peaks (carotid) | AR with AS, HOCM |
| Parvus et tardus 🐢 | Slow-rising, low amplitude | Severe aortic stenosis |
| Bigeminus ♾️ | Couplets; compensatory pause | Ventricular ectopy, digoxin effect/toxicity |
| Pulse deficit ➖ | Apical > radial rate | Atrial fibrillation, frequent ectopy |
| Radio-femoral delay ⏱️ | Femoral later than radial | Coarctation of the aorta |
🧪 JVP & Special Venous Signs (Bedside Hemodynamics)
| Sign | How to Elicit | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatojugular reflux | Firm RUQ pressure 10–15s | ≥3 cm sustained rise in JVP ➝ RV failure / poor reserve |
| Kussmaul’s sign | JVP rises on inspiration | Constrictive pericarditis, RV infarct, restrictive CM |
| Large ‘v’ waves | Visual venous waveform | Tricuspid regurgitation |
🔊 Heart Sounds & Extra Clues
| Sound | Features | Associations |
|---|---|---|
| S3 (“ventricular gallop”) | Early diastole, low-pitched | Volume overload: HF, MR, AR (can be normal <40y) |
| S4 (“atrial kick”) | Late diastole, before S1 | Stiff ventricle: AS, HOCM, HTN; absent in AF |
| Opening snap | After S2 | Mitral stenosis (shorter A2-OS = more severe) |
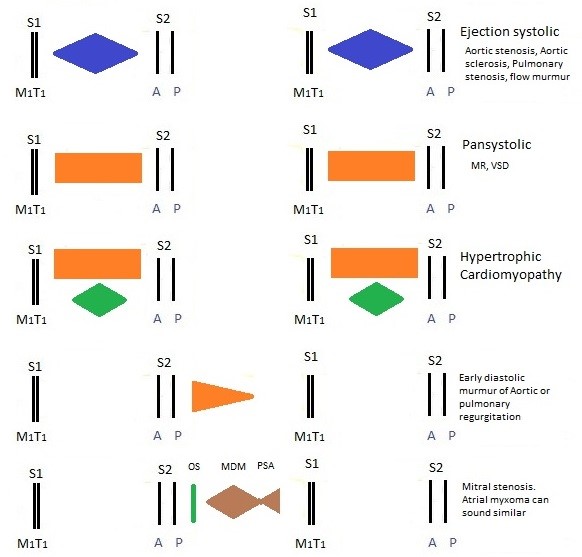
🎧 Murmurs: Sites, Timing, Manoeuvres
| Murmur | Best Site | Timing | Key Clinical Features | Manoeuvres (↑ / ↓) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aortic Stenosis | R 2nd ICS | Systolic ejection | Harsh crescendo–decrescendo; radiates to carotids; narrow pulse pressure; parvus et tardus; angina/syncope/HF | ↑ with squat/leg raise; ↓ with Valsalva/standing |
| Mitral Regurgitation | Apex | Holosystolic | Blowing; to axilla; LA dilatation, AF, pulmonary congestion | ↑ with handgrip; ↑ in left lateral; ↓ with standing |
| Aortic Regurgitation | L 3rd/4th ICS | Early diastolic decrescendo | Best leaning forward at end-expiration; wide PP, collapsing pulse; de Musset; Quincke; may have Austin-Flint at apex | ↑ with handgrip; ↓ with amyl nitrite/vasodilation |
| Mitral Stenosis | Apex | Mid-diastolic rumble | Loud S1 + opening snap; left lateral position; signs of pulmonary HTN, AF, haemoptysis | ↑ with exercise/raising legs; ↓ with tachycardia resolution |
| Tricuspid Regurgitation | LLSB | Holosystolic | ↑ with inspiration (Carvallo); JVP v-waves; RHF signs | ↑ Inspiration; ↓ Expiration/standing |
| Pulmonic Stenosis | L 2nd ICS | Systolic ejection | Harsh; to left shoulder; RV heave; cyanosis if severe | ↑ Inspiration; ↓ Valsalva |
| VSD | LLSB | Harsh holosystolic | Loud without radiation; large shunts ➝ HF, FTT in infants | ↑ Handgrip (↑ afterload); ↓ with vasodilation |
| PDA | Left infraclavicular | Continuous “machine-like” | Bounding pulses; wide PP; may cause HF/PAH | ↑ with handgrip; best in systole-diastole junction |
| HOCM (LVOT) | LLSB/apex | Crescendo systolic | Young pt; S4; may mimic AS but no carotid delay | ↑ Valsalva/standing; ↓ squat/handgrip |
🧑⚕️ Fast Bedside Sequence (Exam Savers)
- Measure BP in both arms (AS/AR; aortic dissection if discrepant).
- Check collapsing pulse (AR) and RR/femoral delay (coarctation).
- JVP at 45°, then HJR if borderline; inspect waveform.
- Apex beat (displaced = volume load; heave = pressure load).
- Listen: all areas + carotids; then targeted manoeuvres (expiration/lean forward for AR; LLDP for MS/MR).
- Lungs for crackles (pulmonary oedema) and periphery for oedema, sacral swelling.
🚩 Do-Not-Miss Pearls
- AF + murmur ➝ think MS/MR; anticoag as indicated.
- Fever + embolic signs (Janeway/Osler/Roth) ➝ IE work-up (3 × blood cultures pre-antibiotics, echo).
- Syncope + ejection murmur in elderly ➝ severe AS until proven otherwise.
- New diastolic murmur is always pathological.
Teaching note: tie the sound to the pressure/volume state. AS = pressure overload (thick LV, slow carotid upstroke). AR/MR = volume overload (displaced, hyperdynamic apex; wide PP in AR). Right-sided murmurs increase with inspiration.
📚 References & Further Reading
- Talley & O’Connor – Clinical Examination
- Geeky Medics OSCE Guides
- OSCEstop Resources