Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Hyperacute Stroke Care Pathway
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Acute Stroke Assessment (ROSIER&NIHSS) |Atrial Fibrillation |Atrial Myxoma |Causes of Stroke |Ischaemic Stroke |Cancer and Stroke |Cardioembolic stroke |CT Basics for Stroke |Endocarditis and Stroke |Haemorrhagic Stroke |Stroke Thrombolysis |Hyperacute Stroke Care
Introduction
- ⏱️ The overriding concept in hyperacute care is that "time is brain." Rapid assessment and intervention are crucial. There are two main patient streams:
- 🚀 Those suitable for urgent, active therapies.
- 🛏️ Those needing general physiological support and prevention of complications.
- Urgent therapies include:
- 💉 Stroke Thrombolysis and 🩻 Mechanical Thrombectomy.
- 🛑 Reversal of anticoagulation in intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH).
- 🧠 Decompression or external ventricular drainage (EVD) for malignant swelling or hydrocephalus.
⏱️ Time is Brain: Every minute of untreated large vessel stroke costs ~1.9 million neurons. Target: CT within 1 hour and thrombolysis within 30 minutes of arrival.
Hospital Care
- 👩⚕️ Stroke-trained staff should rapidly assess patients. Immediate CT is essential for management direction.
- 🎯 Aim for thrombolysis within 20 minutes of arrival by:
- 👋 Greeting patient and taking paramedic handover.
- 🕒 Establishing time of onset and contraindications (esp. anticoagulation).
- 💻 Booking on systems while history/exam done en route to CT.
- 📊 Post-CT: confirm BP, verify weight, and run quick checklist before Alteplase.
- 🔄 Continuous pathway improvement helps reduce door-to-needle times.
| Actions | Comments |
|---|---|
| 🫁 ABC | Airway, breathing, circulation first. Oxygen only if hypoxic. Consider ITU if GCS < 9. Record NIHSS score. |
| 🩸 Blood Glucose | Treat hypoglycaemia immediately (fingerstick test acceptable). |
| 💉 Assess for Thrombolysis | rt-PA within 3 h (>80y) or 4.5 h (<80y). Door-to-needle target: <30 min. |
| 🩻 Assess for Thrombectomy | Mechanical thrombectomy if CTA shows LVO. Best <6 h, can extend to 16–24 h in select cases. |
| 🧠 Haemorrhage / Raised ICP | Consult neurosurgery. Consider EVD, sub-occipital craniectomy (cerebellar bleed), or hemicraniectomy (malignant MCA). |
| 🧪 Haemorrhage with Coagulopathy | Reverse anticoagulation: PCC + Vit K (Warfarin), Praxbind (Dabigatran), platelets if thrombocytopenia. |
Key Information for Thrombolysis/Thrombectomy Referral
| Actions | Comments |
|---|---|
| 👶/👵 Age | <80y → 4.5h window; ≥80y → 3h window. |
| 🕒 Time Since Last Well | Use last well time if onset unclear. |
| 💊 Anticoagulation | Contraindicates thrombolysis ❌ but not thrombectomy ✔️. |
| 📊 NIHSS Score | Reperfusion rarely offered if NIHSS <4 (minor) or >25 (very severe). |
| 🏃 Premorbid State | Benefit less likely if already mRS 4–5 (high dependency). |
| 🩻 CT Report | Avoid referral if CT shows haemorrhage, tumour, or extensive infarction. |
| ⚕️ Comorbidities | Advanced malignancy / recent trauma may contraindicate treatment. |
| 🩺 Blood Pressure | Must be <185/110 mmHg before Alteplase. |
Managing and Preventing Early Complications
| Managing & Preventing Early Complications | |
|---|---|
| 🥤 Swallow Assessment | Screen within 4 h to prevent aspiration pneumonia. |
| 🍽️ Feeding | NG tube if swallow unsafe. |
| 🦵 VTE Prevention | IPC stockings first-line. Avoid LMWH until ICH excluded. |
| 💧 Hydration | IV fluids to prevent dehydration. |
| 🛏️ Skin Care | Regular turns to prevent pressure sores. |
| 🚽 Bowel Care | Prevent constipation. |
| 💪 Shoulder Protection | Support joint to avoid subluxation. |
| 🏃 Therapy | Early mobilisation & rehabilitation. |
| ⚡ Seizure Management | Treat promptly; seizures may indicate large infarct. |
| 🦠 Infection | Treat UTIs & chest infections early. |
| 💧 Bladder Care | Promote continence; avoid catheters if possible. |
📊 Exam pearls: - BP must be <185/110 before thrombolysis. - Hypo- or hyperglycaemia worsens outcome. - Seizures at onset → consider stroke mimic. - Swallow screen within 4 h is a national quality standard.
Schematic of a Pathway
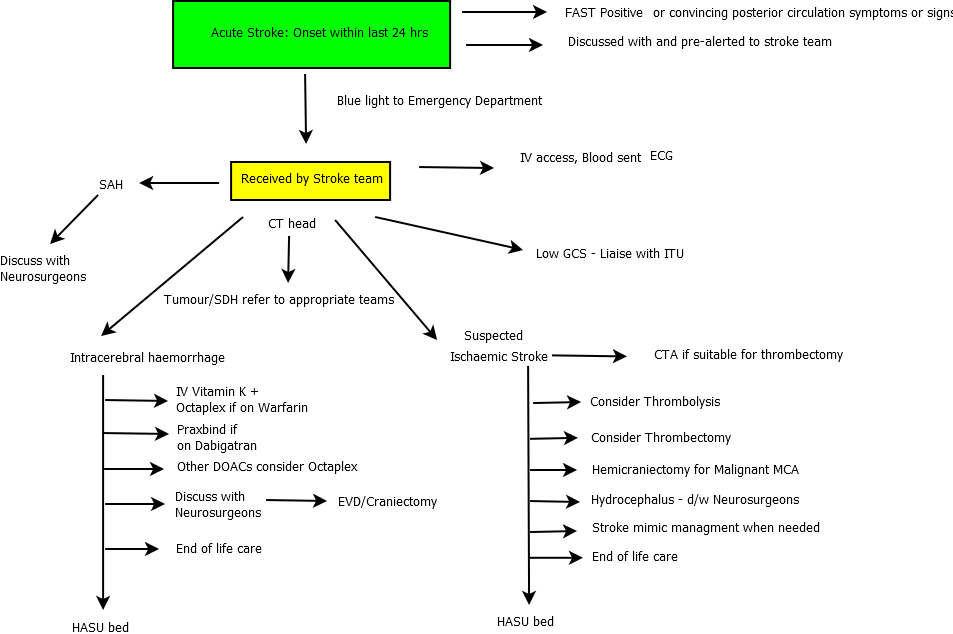
FAST positive → CT within 1 h → Thrombolysis if eligible (<4.5 h) → CTA for thrombectomy if LVO → Admit to HASU for monitoring & prevention.