Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
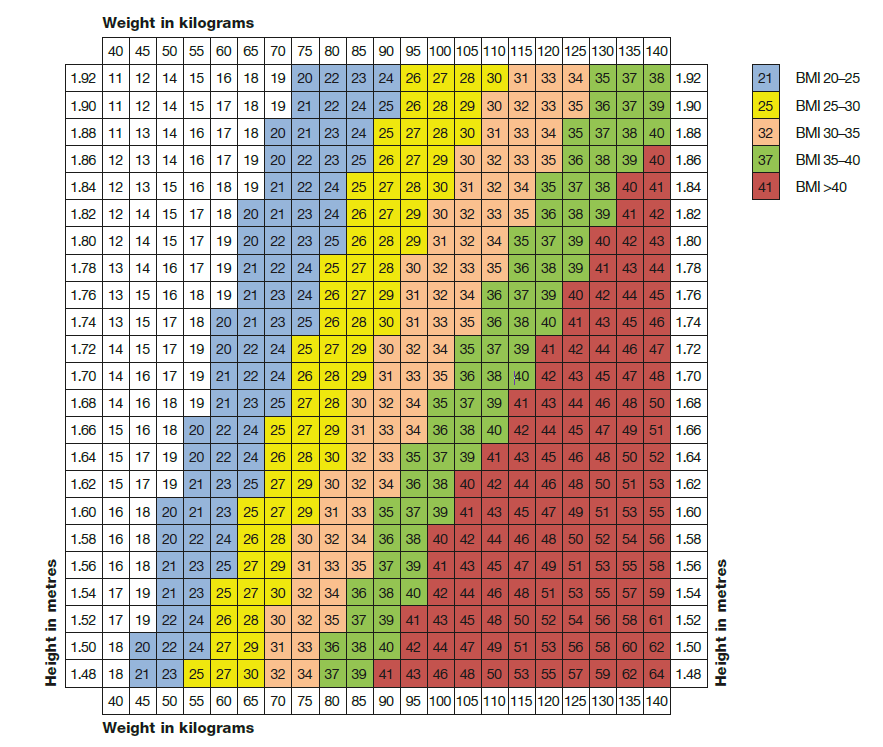
Body Mass Index
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Malnutrition universal screening tool (MUST) |Body Mass Index |Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC) |Refeeding syndrome
📖 Introduction
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a quick and widely used screening tool that relates an individual’s weight to their height, providing a numerical estimate of body fat. Although originally designed for population-level epidemiology by Adolphe Quetelet in the 19th century, it remains a key measure in modern clinical practice and public health. It is especially useful for flagging those at risk of undernutrition, overweight, or obesity, all of which carry significant health implications.
🧮 Calculation and Classification
BMI is calculated using the standard formula:
BMI = Weight (kg) / [Height (m)]2
For adults, BMI is classified into categories (WHO/NICE):
- ⚠️ Underweight: <18.5
- ✅ Normal weight: 18.5 – 24.9
- ⚠️ Overweight: 25 – 29.9
- ⬆️ Obesity Class I: 30 – 34.9
- ⬆️ Obesity Class II: 35 – 39.9
- 🚨 Obesity Class III (Morbid obesity): ≥40
🏥 Clinical Significance
- 📊 Screening tool: Provides a rapid overview of nutritional status in both undernutrition and obesity.
- ❤️ Risk stratification: Higher BMI is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and some cancers.
- 🧩 Monitoring: Useful for following weight changes over time, particularly in patients on weight management programmes or nutritional support.
- 👶 Paediatrics: In children, BMI must be plotted against age- and sex-specific centile charts (UK-WHO growth charts) rather than adult cut-offs.
⚖️ Limitations of BMI
- 💪 Muscle vs fat: BMI does not distinguish lean mass from fat mass, so muscular individuals may appear “overweight.”
- 🧍 Fat distribution: Central obesity (visceral fat) carries more cardiometabolic risk than peripheral fat, but BMI alone cannot capture this.
- 🧓 Age & sex: Elderly patients may have sarcopenia (muscle loss) despite a “normal” BMI. Women generally have higher body fat at the same BMI than men.
- 🌍 Ethnic variation: In South Asian and Chinese populations, health risks occur at lower BMI thresholds → NICE advises using 23 kg/m² as the overweight threshold for these groups.
📌 Alternative / Complementary Measures
- Waist Circumference (WC): Better predictor of central obesity and metabolic syndrome risk. → Risk increased if WC >94 cm (men) or >80 cm (women).
- Waist-to-Height Ratio: >0.5 suggests increased cardiometabolic risk.
- Body Fat %: Measured by bioelectrical impedance or DEXA scanning, gives more accurate assessment of adiposity.
- Clinical context: Combine BMI with blood pressure, lipids, HbA1c, and lifestyle assessment.
🧭 Conclusion
BMI remains a simple, cost-effective, first-line screening tool for assessing nutritional status. However, it should never be used in isolation. Interpreting BMI alongside waist circumference, comorbidities, and demographic factors provides a more accurate picture of health risk. In UK practice, NICE and Public Health England recommend combining BMI with waist measures to guide interventions in obesity and metabolic risk.
📚 References
- NICE CG189: Obesity Identification, Assessment and Management
- WHO – Obesity and Overweight
- Public Health England. Adult Obesity: Applying All Our Health.