Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Viruses and their infections
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Bacteria and their Infections |Viruses and their Infections |Herpes Varicella-Zoster (Shingles) Infection |Chickenpox Varicella Infection |Varicella Cerebral Vasculopathy |Herpes Viruses |Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO) Shingles |MonkeyPox |Mumps |Measles |Rubella (German Measles) |Epstein-Barr Virus infection
Viruses are microscopic infectious agents that require a host cell to replicate. They consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat called a capsid, and sometimes an outer lipid envelope. Viruses infect all types of life forms, including animals, plants, and microorganisms, and are responsible for a wide range of diseases in humans.
Viral Structure
- Nucleic Acid :
- Contains either DNA or RNA, which can be single-stranded or double-stranded.
- Encodes the genetic information necessary for viral replication and protein synthesis.
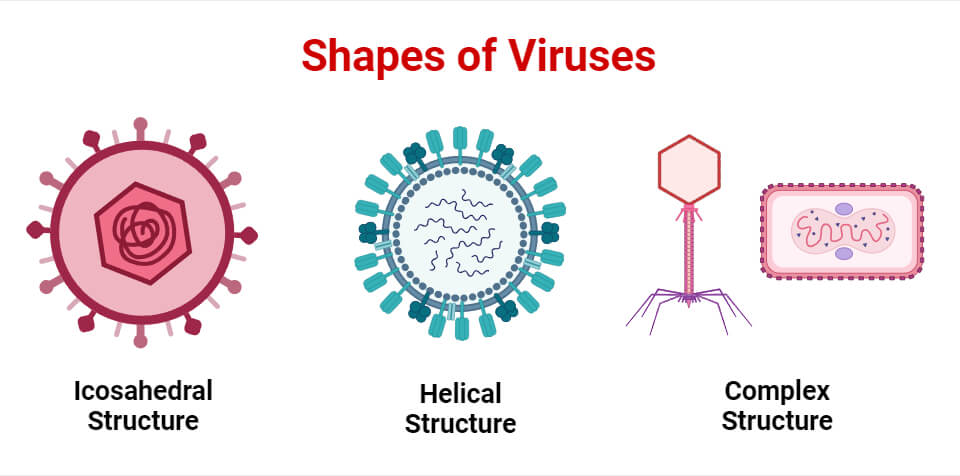
- Capsid :
- A protective protein coat surrounding the nucleic acid.
- Composed of protein subunits called capsomeres, arranged in shapes like helical, icosahedral, or complex structures.
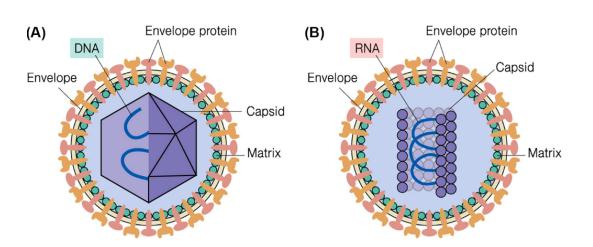
- Envelope (in some viruses):
- A lipid bilayer derived from the host cell membrane.
- Contains viral glycoproteins essential for host cell recognition and entry.
Viral Life Cycle
- Attachment :
- Viruses attach to specific receptors on the host cell surface.
- This determines host specificity and which tissues the virus can infect (tissue tropism).
- Entry :
- Viral particles or their genomes enter the host cell via fusion, endocytosis, or direct penetration.
- Replication and Transcription :
- The viral genome is replicated using the host cell's machinery.
- Viral genes are transcribed into mRNA, directing the synthesis of viral proteins.
- Translation and Protein Synthesis :
- Host ribosomes translate viral mRNA to produce viral proteins.
- Assembly :
- New viral particles are assembled from the replicated genome and synthesized proteins.
- Release :
- New viruses are released to infect new cells, either by cell lysis, budding, or exocytosis.
Viral Pathogenesis
- Entry and Initial Replication :
- Viruses enter through mucosal surfaces, skin breaches, or direct inoculation.
- They begin replicating at the site of entry, potentially leading to local symptoms.
- Spread and Dissemination :
- Viruses spread locally or systemically via the bloodstream (viremia) or lymphatic system.
- Cellular Damage and Immune Response :
- Direct damage includes cell lysis, apoptosis, or fusion of cells into syncytia.
- Indirect damage is mediated by immune responses, causing inflammation and cytokine release.
- Clinical Manifestations :
- Acute infections : Rapid onset, such as influenza or common cold.
- Chronic infections : Persistent infections, such as HIV or hepatitis B.
- Latent infections : Dormant virus with potential reactivation, such as herpes simplex.
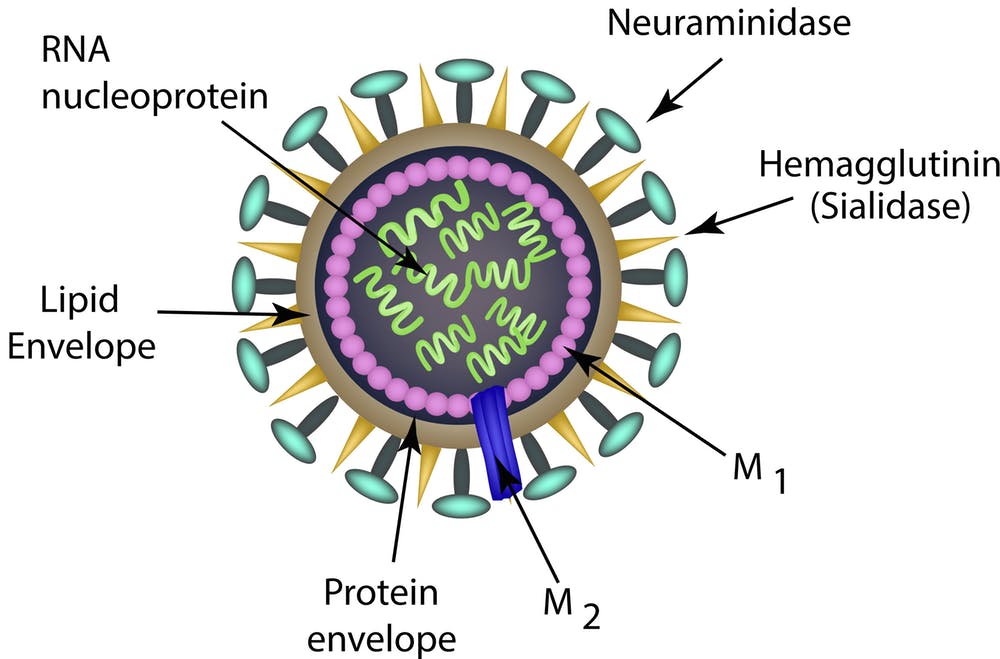 Influenza
Influenza
Host Immune Response
- Innate Immunity :
- First line of defense with physical barriers, phagocytes, natural killer cells, and interferons.
- Interferons inhibit viral replication and activate immune cells.
- Adaptive Immunity :
- Humoral immunity : B cells produce antibodies to neutralize viruses and promote their clearance.
- Cell-mediated immunity : Cytotoxic T cells kill infected cells; helper T cells coordinate the response.
- Immune Evasion Strategies :
- Viruses evade immunity by antigenic variation, inhibiting antigen presentation, and latency.
Examples of Viral Diseases
- Influenza :
- Caused by influenza viruses (types A, B, and C).
- Characterized by fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, and fatigue.
- Prevention includes vaccination and antiviral medications.
- HIV/AIDS :
- Caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
- Targets CD4+ T cells, leading to immune system failure and susceptibility to infections and cancers.
- Managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART).
- Hepatitis :
- Caused by hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, and E).
- Results in liver inflammation, fibrosis, and potential cirrhosis or cancer.
- Prevention includes vaccination (for hepatitis A and B) and antiviral treatments (for hepatitis B and C).
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infections :
- Caused by HSV-1 and HSV-2, resulting in recurrent painful vesicular eruptions.
- Treatment includes antivirals to reduce outbreak severity and frequency.
- COVID-19 :
- Caused by SARS-CoV-2, leading to symptoms from mild respiratory illness to severe ARDS.
- Prevention includes vaccination, social distancing, and masks.
Clinical and Diagnostic Approaches
- Laboratory Diagnosis :
- Virus isolation, PCR (polymerase chain reaction), and serology for detecting antibodies/antigens.
- Imaging Techniques :
- Radiography, CT, and MRI to assess organ involvement.
- Therapeutic Interventions :
- Antiviral medications, immunomodulatory agents, and supportive care.
- Preventive Measures :
- Vaccination and public health measures, including sanitation and vector control.
Summary
Viruses are small infectious agents reliant on host cells for replication. They have diverse structures and life cycles, causing a wide array of diseases in humans. Understanding viral structure, pathogenesis, and the immune response is essential for diagnosing, treating, and preventing infections. Advances in antiviral therapies and vaccines continue to enhance our ability to manage viral diseases effectively.
Viral Diseases
| Viral Infection | Clinical Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Influenza (Flu) |
|
|
| Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1, HSV-2) |
|
|
| Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) |
|
|
| Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) |
|
|
| Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) |
|
|
| HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) |
|
|
| Measles (Rubeola) |
|
|
| Human Papillomavirus (HPV) |
|
|
| Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) |
|
|