Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |

|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. | |
Medulla Oblongata
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |Medulla Oblongata |Midbrain |Pons |Caudate Nucleus |Putamen and Globus Pallidus |Cerebral Cortex |Internal Capsule |Cavernous sinus
Overview of the Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata is a portion of the brainstem located between the pons and the spinal cord. It plays a critical role in regulating vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure, and serves as a conduit for neural pathways between the brain and spinal cord.
Anatomy of the Medulla Oblongata
- The medulla oblongata is approximately 3 cm long and is divided into:
- Anterior (Ventral) Surface:
- Contains the pyramids, which are two longitudinal ridges formed by corticospinal tracts.
- The pyramidal decussation is where most of the fibers cross to the opposite side, explaining why each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body.
- Posterior (Dorsal) Surface:
- Contains the gracile and cuneate tubercles, which are associated with the gracile and cuneate nuclei involved in sensory processing.
- Internal Structure:
- Comprised of ascending and descending tracts, cranial nerve nuclei, and various autonomic nuclei.
- Anterior (Ventral) Surface:
Functions of the Medulla Oblongata
- Autonomic Functions:
- The medulla oblongata contains vital autonomic centres that regulate essential physiological processes.
- Cardiovascular Center:
- Regulates heart rate, force of contraction, and blood vessel diameter.
- Includes the cardiac centre (controls heart rate) and the vasomotor centre (regulates blood pressure).
- Respiratory Center:
- Controls the rate and depth of breathing.
- Works in conjunction with the pons to maintain rhythmic breathing patterns.
- Cardiovascular Center:
- The medulla oblongata contains vital autonomic centres that regulate essential physiological processes.
- Reflex Centers:
- Coordinates several reflex actions, including swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and vomiting.
- Cranial Nerve Nuclei:
- Houses nuclei for several cranial nerves (IX - glossopharyngeal, X - vagus, XI - accessory, XII - hypoglossal), which control various motor and sensory functions in the head and neck.
- Pathways for Neural Signals:
- The medulla oblongata contains tracts that transmit signals between the brain and the spinal cord, including:
- Ascending Tracts: Carry sensory information from the body to the brain.
- Descending Tracts: Transmit motor commands from the brain to the body.
- The medulla oblongata contains tracts that transmit signals between the brain and the spinal cord, including:
Clinical Relevance
- Medullary Syndromes:
- Infarctions or lesions in the medulla oblongata can lead to various syndromes, such as:
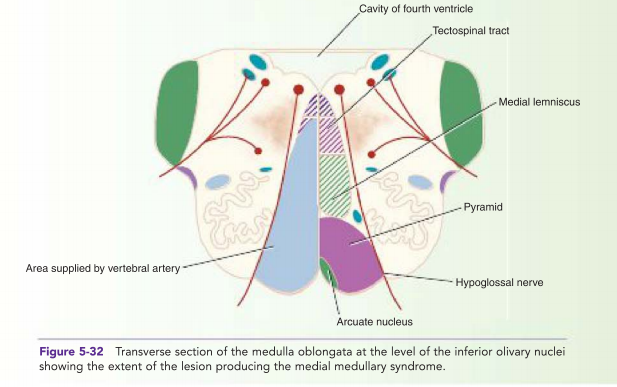
- Medial Medullary Syndrome (Dejerine Syndrome): Caused by infarction of the anterior spinal artery, leading to contralateral hemiparesis, contralateral loss of proprioception and vibration, and ipsilateral hypoglossal nerve dysfunction.
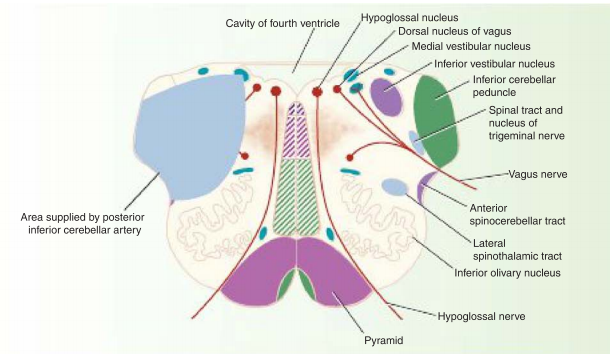
- Lateral Medullary Syndrome (Wallenberg Syndrome): Results from occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA), causing ipsilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation on the face, contralateral loss on the body, dysphagia, hoarseness, and ataxia.
- Infarctions or lesions in the medulla oblongata can lead to various syndromes, such as:
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular Dysfunction:
- Damage to the medullary respiratory or cardiovascular centres can lead to life-threatening conditions such as respiratory failure or cardiac arrest.
- Herniations:
- Increased intracranial pressure can cause brain tissue to herniate through the foramen magnum, compressing the medulla oblongata and potentially resulting in fatal outcomes.
Summary
The medulla oblongata is a critical structure within the brainstem that regulates vital autonomic functions, including cardiovascular and respiratory control. Its role in reflex actions and as a conduit for neural pathways underscores its importance in maintaining homeostasis and responding to various physiological demands. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the medulla oblongata is essential for diagnosing and managing conditions that affect this crucial part of the brain.